Comparative analysis of ribosomal proteins in complete genomes: an example of reductive evolution at the domain scale
- PMID: 12490706
- PMCID: PMC140077
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkf693
Comparative analysis of ribosomal proteins in complete genomes: an example of reductive evolution at the domain scale
Abstract
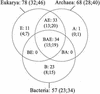
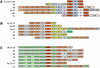
A comprehensive investigation of ribosomal genes in complete genomes from 66 different species allows us to address the distribution of r-proteins between and within the three primary domains. Thirty-four r-protein families are represented in all domains but 33 families are specific to Archaea and Eucarya, providing evidence for specialisation at an early stage of evolution between the bacterial lineage and the lineage leading to Archaea and Eukaryotes. With only one specific r-protein, the archaeal ribosome appears to be a small-scale model of the eukaryotic one in terms of protein composition. However, the mechanism of evolution of the protein component of the ribosome appears dramatically different in Archaea. In Bacteria and Eucarya, a restricted number of ribosomal genes can be lost with a bias toward losses in intracellular pathogens. In Archaea, losses implicate 15% of the ribosomal genes revealing an unexpected plasticity of the translation apparatus and the pattern of gene losses indicates a progressive elimination of ribosomal genes in the course of archaeal evolution. This first documented case of reductive evolution at the domain scale provides a new framework for discussing the shape of the universal tree of life and the selective forces directing the evolution of prokaryotes.
Figures


References
-
- Wimberly B.T., Brodersen,D.E., Clemons,W.M.,Jr, Morgan-Warren,R.J., Carter,A.P., Vonrhein,C., Hartsch,T. and Ramakrishnan,V. (2000) Structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit. Nature, 407, 327–339. - PubMed
-
- Schluenzen F., Tocilj,A., Zarivach,R., Harms,J., Gluehmann,M., Janell,D., Bashan,A., Bartels,H., Agmon,I., Franceschi,F. et al. (2000) Structure of functionally activated small ribosomal subunit at 3.3 angstroms resolution. Cell, 102, 615–623. - PubMed
-
- Harms J., Schluenzen,F., Zarivach,R., Bashan,A., Gat,S., Agmon,I., Bartels,H., Franceschi,F. and Yonath,A. (2001) High resolution structure of the large ribosomal subunit from a mesophilic eubacterium. Cell, 107, 679–688. - PubMed
-
- Ban N., Nissen,P., Hansen,J., Moore,P.B. and Steitz,T.A. (2000) The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 Å resolution. Science, 289, 905–920. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

