Oral immunization with ATP-dependent protease-deficient mutants protects mice against subsequent oral challenge with virulent Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium
- PMID: 12496146
- PMCID: PMC143154
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.1.30-39.2003
Oral immunization with ATP-dependent protease-deficient mutants protects mice against subsequent oral challenge with virulent Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium
Abstract
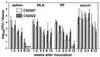
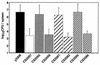
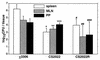
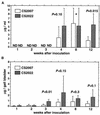
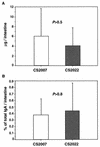
We evaluated the efficacy of mutants with a deletion of the stress response protease gene as candidates for live oral vaccine strains against Salmonella infection through infection studies with mice by using a Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium mutant with a disruption of the ClpXP or Lon protease. In vitro, the ClpXP protease regulates flagellum synthesis and the ClpXP-deficient mutant strain exhibits hyperflagellated bacterial cells (T. Tomoyasu et al., J. Bacteriol. 184:645-653, 2002). On the other hand, the Lon protease negatively regulates the efficacy of invading epithelial cells and the expression of invasion genes (A. Takaya et al., J. Bacteriol. 184:224-232, 2002). When 5-week-old BALB/c mice were orally administered 5 x 10(8) CFU of the ClpXP- or Lon-deficient strain, bacteria were detected with 10(3) to 10(4) CFU in the spleen, mesenteric lymph nodes, Peyer's patches, and cecum 1 week after inoculation and the bacteria then decreased gradually in each tissue. Significant increases of lipopolysaccharide-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) and secretory IgA were detected at week 4 and maintained until at least week 12 after inoculation in serum and bile, respectively. Immunization with the ClpXP- or Lon-deficient strain protected mice against oral challenge with the serovar Typhimurium virulent strain. Both the challenged virulent and immunized avirulent salmonellae were completely cleared from the spleen, mesenteric lymph nodes, Peyer's patches, and even cecum 5 days after the challenge. These data indicate that Salmonella with a disruption of the ATP-dependent protease ClpXP or Lon can be useful in developing a live vaccine strain.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Salmonella flagellin is not a dominant protective antigen in oral immunization with attenuated live vaccine strains.Infect Immun. 2004 Apr;72(4):2449-51. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.4.2449-2451.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15039380 Free PMC article.
-
Lon, a stress-induced ATP-dependent protease, is critically important for systemic Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium infection of mice.Infect Immun. 2003 Feb;71(2):690-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.2.690-696.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12540547 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse models for assessing the cross-protective efficacy of oral non-typhoidal Salmonella vaccine candidates harbouring in-frame deletions of the ATP-dependent protease lon and other genes.J Med Microbiol. 2015 Mar;64(Pt 3):295-302. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000014. Epub 2015 Jan 14. J Med Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25589672
-
Live Attenuated Human Salmonella Vaccine Candidates: Tracking the Pathogen in Natural Infection and Stimulation of Host Immunity.EcoSal Plus. 2016 Nov;7(1):10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0010-2016. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0010-2016. EcoSal Plus. 2016. PMID: 27809955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Attenuating gene expression (AGE) for vaccine development.Virulence. 2013 Jul 1;4(5):384-90. doi: 10.4161/viru.24886. Epub 2013 May 7. Virulence. 2013. PMID: 23652809 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in the development of Salmonella-based vaccine strategies for protection against Salmonellosis in humans.J Appl Microbiol. 2021 Dec;131(6):2640-2658. doi: 10.1111/jam.15055. Epub 2021 Apr 3. J Appl Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33665941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the live vaccine efficacy of virulence plasmid-cured, and phoP- or aroA-deficient Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in mice.J Vet Med Sci. 2015 Feb;77(2):181-6. doi: 10.1292/jvms.14-0013. Epub 2014 Oct 24. J Vet Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 25341392 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial proteases, untapped antimicrobial drug targets.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2017 Apr;70(4):366-377. doi: 10.1038/ja.2016.138. Epub 2016 Nov 30. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2017. PMID: 27899793 Review.
-
Comparative efficacies of different antibiotic treatments to eradicate nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae infection.BMC Infect Dis. 2008 Feb 7;8:15. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-8-15. BMC Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18254980 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella Typhimurium TTSS-2 deficient mig-14 mutant shows attenuation in immunocompromised mice and offers protection against wild-type Salmonella Typhimurium infection.BMC Microbiol. 2013 Oct 22;13:236. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-236. BMC Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24148706 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asakura, S., G. Eguchi, and T. Iino. 1964. Reconstitution of bacterial flagella in vitro. J. Mol. Biol. 10:42-56. - PubMed
-
- Brown, A., and C. E. Hormaeche. 1989. The antibody response to salmonellae in mice and humans studied by immunoblots and ELISA. Microb. Pathog. 6:445-454. - PubMed
-
- Brown, G. D., and S. Gordon. 2002. Phagocytes and anti-infective immunity, p. 79-91. In S. E. Kaufmann, A. Sher, and R. Ahmed (ed.), Immunology of infectious diseases. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C.
-
- Buchmeier, N., S. Bossie, C.-Y. Chen, F. C. Fang, D. G. Guiney, and S. J. Libby. 1997. SlyA, a transcriptional regulator of Salmonella typhimurium, is required for resistance to oxidative stress and is expressed in the intracellular environment of macrophages. Infect. Immun. 65:3725-3730. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chatfield, S. N., K. Strahan, D. Pickard, I. G. Charles, C. E. Hormaeche, and G. Dougan. 1992. Evaluation of Salmonella typhimurium strains harbouring defined mutations in htrA and aroA in the murine salmonellosis model. Microb. Pathog. 12:145-151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

