Two-component systems in Haemophilus influenzae: a regulatory role for ArcA in serum resistance
- PMID: 12496162
- PMCID: PMC143216
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.1.163-172.2003
Two-component systems in Haemophilus influenzae: a regulatory role for ArcA in serum resistance
Abstract
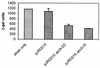
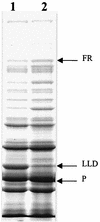
Knockout mutations were constructed in the arcA gene of a virulent type b strain of Haemophilus influenzae, and the behavior of the resulting mutants was investigated in a number of conditions that mimicked distinct steps in the natural infection pathway. In arcA mutants, synthesis of capsule and lipooligosaccharide (LOS) and growth in synthetic media were unaltered compared to synthesis of capsule and LOS and growth in synthetic media in the wild-type H. influenzae type b parent strain. However, the virulence of the arcA mutants for BALB/c mice was significantly reduced. Upon exposure to human blood or serum, the arcA mutants showed markedly reduced survival compared with the survival of its wild-type parent. Serum resistance could be fully restored by complementation in cis with the H. influenzae arcA gene but not by complementation in cis with the homologous gene from Escherichia coli. The proteomes of wild-type and mutant bacteria were markedly different, especially under anaerobic conditions, underscoring the global regulatory role of ArcAB in H. influenzae. Evaluation of antibody titers and classical complement activities in various serum samples pointed to complement-mediated bactericidal activity as the factor that distinguishes between the arcA mutant and wild-type phenotypes. Comparative analysis of the membrane fractions of the arcA mutants and the wild-type strain revealed several ArcA-regulated proteins, some of which may be implicated in the serum hypersensitivity phenotype.
Figures





References
-
- Appel, R. D., P. M. Palagi, D. Walther, J. R. Vargas, J.-C. Sanchez, F. Ravier, C. Pasquali, and D. F. Hochstrasser. 1997. Melanie II—a third-generation software package for analysis of two-dimensional electrophoresis images. I. Features and user interface. Electrophoresis 18:2724-2734. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj, V., R. L. Lucas, C. Hwang, and C. A. Lee. 1996. Co-ordinate regulation of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes by environmental and regulatory factors is mediated by control of hilA expression. Mol. Microbiol. 22:703-714. - PubMed
-
- Barcak, G. J., M. S. Chandler, R. J. Redfield, and J.-F. Tomb. 1991. Genetic systems in Haemophilus influenzae. Methods Enzymol. 204:321-342. - PubMed
-
- Barra, A., R. Dagan, J. L. Preud'homme, A. Bajart, B. Danve, and B. Fritzell. 1993. Characterization of the serum antibody response induced by Haemophilus influenzae type b tetanus protein-conjugate vaccine in infants receiving a DTP-combined vaccine from 2 months of age. Vaccine 11:1003-1006. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

