Purification and characterization of a UDP-glucosyltransferase produced by Legionella pneumophila
- PMID: 12496164
- PMCID: PMC143419
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.1.181-186.2003
Purification and characterization of a UDP-glucosyltransferase produced by Legionella pneumophila
Abstract
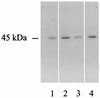
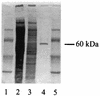
Legionella pneumophila is the agent of Legionnaires' disease. It invades and replicates within eukaryotic cells, including aquatic protozoans, mammalian macrophages, and epithelial cells. The molecular mechanisms of the Legionella interaction with target cells are not fully defined. In an attempt to discover novel virulence factors of L. pneumophila, we searched for bacterial enzymes with transferase activity. Upon screening ultrasonic extracts of virulent legionellae, we identified a uridine diphospho (UDP)-glucosyltransferase activity, which was capable of modifying a 45-kDa substrate in host cells. An approximately 60-kDa UDP-glucosyltransferase was purified from L. pneumophila and subjected to microsequencing. An N-terminal amino acid sequence, as well as the sequence of an internal peptide, allowed us to identify the gene for the enzyme within the unfinished L. pneumophila genome database. The intact gene was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli, and the recombinant protein was purified and confirmed to possess an enzymatic activity similar to that of the native UDP-glucosyltransferase. We designated this gene ugt (UDP-glucosyltransferase). The Legionella enzyme did not exhibit significant homology with any known protein, suggesting that it is novel in structure and, perhaps, in function. Based on PCR data, an enzyme assay, and an immunoblot analysis, the glucosyltransferase appeared to be conserved in L. pneumophila strains but was absent from the other Legionella species. This study represents the first identification of a UDP-glucosyltransferase in an intracellular parasite, and therefore modification of a eukaryotic target(s) by this enzyme may influence host cell function and promote L. pneumophila proliferation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Legionella pneumophila glucosyltransferase inhibits host elongation factor 1A.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Nov 7;103(45):16953-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0601562103. Epub 2006 Oct 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17068130 Free PMC article.
-
Lgt: a family of cytotoxic glucosyltransferases produced by Legionella pneumophila.J Bacteriol. 2008 Apr;190(8):3026-35. doi: 10.1128/JB.01798-07. Epub 2008 Feb 15. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18281405 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and Analysis of Effector Glucosyltransferase Lgt1 from Legionella pneumophila.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1921:277-287. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9048-1_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30694499
-
Genetics and molecular pathogenesis of Legionella pneumophila, an intracellular parasite of macrophages.Mol Biol Med. 1989 Oct;6(5):409-24. Mol Biol Med. 1989. PMID: 2696860 Review.
-
Analysis of virulence factors of Legionella pneumophila.Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1993 Apr;278(2-3):348-58. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80851-0. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1993. PMID: 8347938 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of ubiquitin dynamics and suppression of DALIS formation by the Legionella pneumophila Dot/Icm system.Cell Microbiol. 2009 Feb;11(2):261-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01251.x. Epub 2008 Nov 4. Cell Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19016782 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of elongation factor 1A inhibition by a Legionella pneumophila glycosyltransferase.Biochem J. 2010 Feb 24;426(3):281-92. doi: 10.1042/BJ20091351. Biochem J. 2010. PMID: 20030628 Free PMC article.
-
Legionella pneumophila-mediated host posttranslational modifications.J Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Nov 27;15(5):mjad032. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjad032. J Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37156500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Legionella pneumophila glucosyltransferase inhibits host elongation factor 1A.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Nov 7;103(45):16953-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0601562103. Epub 2006 Oct 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17068130 Free PMC article.
-
The Legionella pneumophila Metaeffector Lpg2505 (MesI) Regulates SidI-Mediated Translation Inhibition and Novel Glycosyl Hydrolase Activity.Infect Immun. 2020 Apr 20;88(5):e00853-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00853-19. Print 2020 Apr 20. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 32122942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aragon, V., O. Rossier, and N. P. Cianciotto. 2002. Legionella pneumophila genes that encode lipase and phospholipase C activities. Microbiology 148:2223-2231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

