Selective early production of CCL20, or macrophage inflammatory protein 3alpha, by human mast cells in response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 12496186
- PMCID: PMC143158
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.1.365-373.2003
Selective early production of CCL20, or macrophage inflammatory protein 3alpha, by human mast cells in response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
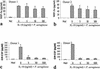
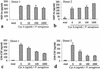
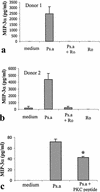
Mast cells are important as sentinel cells in host defense against bacterial infection. Much of their effectiveness depends upon recruiting other immune cells; however, little is known about the mechanisms of this response. CCL20, also known as macrophage inflammatory protein-3alpha (MIP-3alpha), Exodus, and LARC, is a chemokine known to be a potent chemoattractant for immature dendritic cells and T cells. In this study, we examined the human mast cell production of both CCL20 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), a critical cytokine for innate immune responses in the lung, in response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Reverse transcription-PCR and Western blot analysis demonstrated that the human mast cells (HMC-1) express CCL20 mRNA and are able to produce a significant amount (32.4 ng/ml) of CCL20 protein following stimulation by calcium ionophore and phorbol myristate acetate. Importantly, P. aeruginosa potently stimulated CCL20 production in human cord blood-derived mast cells (CBMC), with production peaking at 6 h after stimulation. This time course of expression was distinct from that of GM-CSF, which peaked after 24 to 48 h. Significant CCL20 production did not occur following immunoglobulin E-mediated activation of CBMC under conditions which induced a substantial GM-CSF response. Interestingly, the CCL20 response of mast cells to P. aeruginosa was relatively resistant to inhibition by the corticosteroid dexamethasone, interleukin-10, or cyclosporine, while GM-CSF production was potently inhibited. However, P. aeruginosa-induced CCL20 production was blocked by the protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor Ro 31-8220 and a PKC pseudosubstrate. These results support a role for human mast cells in the initiation of immune responses to P. aeruginosa infection.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Airway epithelial cells release MIP-3alpha/CCL20 in response to cytokines and ambient particulate matter.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003 Jun;28(6):648-54. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2002-0095OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12760962
-
Regulated production and molecular diversity of human liver and activation-regulated chemokine/macrophage inflammatory protein-3 alpha from normal and transformed cells.J Immunol. 2000 Oct 15;165(8):4470-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.8.4470. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11035086
-
The CC chemokine CCL20 and its receptor CCR6.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003 Oct;14(5):409-26. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(03)00049-2. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003. PMID: 12948524 Review.
-
Neutrophils produce biologically active macrophage inflammatory protein-3alpha (MIP-3alpha)/CCL20 and MIP-3beta/CCL19.Eur J Immunol. 2001 Jul;31(7):1981-8. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200107)31:7<1981::aid-immu1981>3.0.co;2-x. Eur J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11449350
-
The airway epithelium as immune modulator: the LARC ascending.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003 Jun;28(6):641-4. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.F271. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12760960 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Mast cell plasticity and sphingosine-1-phosphate in immunity, inflammation and cancer.Mol Immunol. 2015 Jan;63(1):104-12. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2014.03.018. Epub 2014 Apr 22. Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 24766823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human transcriptomic response to periprosthetic joint infection.Gene. 2022 May 30;825:146400. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.146400. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Gene. 2022. PMID: 35306116 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoids enhance or spare innate immunity: effects in airway epithelium are mediated by CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins.J Immunol. 2007 Jul 1;179(1):578-89. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.1.578. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17579079 Free PMC article.
-
The P2Y11 receptor of human M2 macrophages activates canonical and IL-1 receptor signaling to translate the extracellular danger signal ATP into anti-inflammatory and pro-angiogenic responses.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Sep 15;79(10):519. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04548-z. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36107259 Free PMC article.
-
CCL20 induced by visfatin in macrophages via the NF-κB and MKK3/6-p38 signaling pathways contributes to hepatic stellate cell activation.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Jun;47(6):4285-4293. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05510-7. Epub 2020 May 16. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32418112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baba, M., T. Imai, M. Nishimura, M. Kakizaki, S. Takagi, K. Hieshima, H. Nomiyama, and O. Yoshie. 1997. Identification of CCR6, the specific receptor for a novel lymphocyte-directed CC chemokine LARC. J. Biol. Chem. 272:14893-14898. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann, U., J. Scheffer, M. Koller, W. Schonfeld, G. Erbs, F. E. Muller, and W. Konig. 1989. Induction of inflammatory mediators (histamine and leukotrienes) from rat peritoneal mast cells and human granulocytes by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains from burn patients. Infect. Immun. 57:2187-2195. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

