Rat-to-human transmission of Cowpox infection
- PMID: 12498670
- PMCID: PMC2738512
- DOI: 10.3201/eid0812.020089
Rat-to-human transmission of Cowpox infection
Abstract
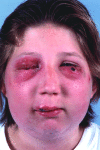
We isolated Cowpox virus (CPXV) from the ulcerative eyelid lesions of a 14-year-old girl, who had cared for a clinically ill wild rat that later died. CPXV isolated from the rat (Rattus norvegicus) showed complete homology with the girl's virus. Our case is the first proven rat-to-human transmission of cowpox.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
