Correlation of phenotypic zidovudine resistance with mutational patterns in the reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: interpretation of established mutations and characterization of new polymorphisms at codons 208, 211, and 214
- PMID: 12499169
- PMCID: PMC149009
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.1.54-61.2003
Correlation of phenotypic zidovudine resistance with mutational patterns in the reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: interpretation of established mutations and characterization of new polymorphisms at codons 208, 211, and 214
Abstract
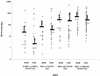
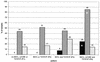
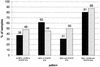
Zidovudine resistance (ZDV-R) is associated with classic genotypic changes at codons 41, 67, 70, 210, 215, and 219 of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) reverse transcriptase (RT) gene as well as with the multinucleoside resistance (MNR) complexes (Q151M MNR complex; 6-bp insertion/A62V complex). In addition, enhanced resistance to ZDV in the context of the classic ZDV mutations plus the M184V mutation has been associated with additional mutations at positions 208, 211, 214, and 333. In this study we investigated phenotypic ZDV-R determined by a recombinant virus assay (Antivirogram; Virco) in 223 clinical samples in relation to the above genotypic changes. 150 out of 223 clinical samples had the M184V mutation. Phenotypic ZDV-R ranged from 0.3- to 5,338-fold. Sixteen samples (15 with high ZDV-R ranging from 90- to 3,571-fold) contained MNR-associated patterns. Analysis of classic mutational patterns broadly demonstrated increasing ZDV-R with increasing number of ZDV mutations. A comparable correlation was obtained when ZDV-R was analyzed only relative to the T215Y/F mutation. Site-directed mutagenesis experiments investigating the influence of the additional mutations H208Y, R211K, and L214F on ZDV-R resulted in a 7.4- or 21-fold increase in ZDV-R when the R211K/L214F or H208Y/R211K/L214F mutations, respectively, were added to a highly ZDV-R virus. In the clinical sample data set we analyzed, the combination of R211K/L214F appeared most frequently. The H208Y change was detected only in highly ZDV-R viruses, whereas the G333E/D change was distributed equally. All changes were independent of the M184V mutation. A 2.4- or 8-fold increase in ZDV-R was observed in the clinical samples with high ZDV-R containing the R211K/L214F or H208Y/R211K/L214F mutations, respectively. We have shown that the combination of the additional mutations H208Y, R211K, and L214F in HIV-1 RT may influence ZDV-R and should be considered when assessing ZDV-R.
Figures

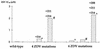
Comment in
-
Human immunodeficiency virus polymorphisms and zidovudine resistance.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003 Aug;47(8):2714; author reply 2714-5. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.8.2714-2715.2003. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. PMID: 12878551 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Boucher, C. A., N. Cammack, P. Schipper, R. Schuurman, P. Rouse, M. A. Wainberg, and J. M. Cameron. 1993. High-level resistance to (−) enantiomeric 2′-deoxy-3′-thiacytidine in vitro is due to one amino acid substitution in the catalytic site of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 37:2231-2234. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen, P., J. C. Schmit, V. Arendt, J. M. Plesseria, C. Lambert, E. Fontaine, P. Kirpach, D. Ninove, F. Schneider, and R. Hemmer. 1997. Drug resistance mutations as predictors of phenotypic zidovudine resistance in HIV-1 infection. AIDS 11:1528-1529. - PubMed
-
- De Antoni, A., A. Foli, J. Lisziewicz, and F. Lori. 1997. Mutations in the pol gene of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in infected patients receiving didanosine and hydroxyurea combination therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 176:899-903. - PubMed
-
- De Jong, J. J., J. Goudsmit, V. V. Lukasov, M. E. Hillebrand, E. Baan, R. Huismans, S. A. Danner, J. H. Ten Veen, F. De Wolf, and S. Jurriaans. 1999. Insertion of two amino acids combined with changes in reverse transcriptase containing tyrosine-215 of HIV-1 resistant to multiple nucleoside analogs. AIDS 13:75-80. - PubMed
-
- Fischl, M. A., D. D. Richman, M. H. Grieco, M. S. Gottlieb, P. A. Volberding, O. L. Laskin, J. M. Leedom, J. E. Groopman, D. Mildvan, R. T. Schooley, G. G. Jackson, D. T. Durack, D. King, and The ZDV Collaborative Working Group. 1987. The efficacy of azidothymidine (ZDV) in the treatment of patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. N. Engl. J. Med. 317:185-191. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

