Comparison of linezolid activities under aerobic and anaerobic conditions against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium
- PMID: 12499223
- PMCID: PMC148952
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.1.398-399.2003
Comparison of linezolid activities under aerobic and anaerobic conditions against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium
Abstract
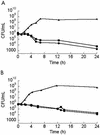
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium were exposed to linezolid (MIC of 2 mg/liter) under aerobic or anaerobic conditions in an in vitro pharmacodynamic model. Drug concentration and half-life were adjusted to simulate clinical dosing (600 mg twice daily) of linezolid. Linezolid produced a 2-log(10) killing at 24 h, and rates of killing against each of these facultative organisms as measured by mean survival time appeared similar under aerobic and anaerobic conditions.
Figures
References
-
- Peterson, L. R., and D. N. Gerding. 1980. Influence of protein binding of antibiotics on serum pharmacokinetics and extravascular penetration: clinically useful concepts. Rev. Infect. Dis. 2:340-348. - PubMed
-
- Suller, M. T., and D. Lloyd. 2002. The antibacterial activity of vancomycin towards Staphylococcus aureus under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. J. Appl. Microbiol. 92:866-872. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources