Activation and deactivation of a broad-spectrum antiviral drug by a single enzyme: adenosine deaminase catalyzes two consecutive deamination reactions
- PMID: 12499231
- PMCID: PMC149024
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.1.426-431.2003
Activation and deactivation of a broad-spectrum antiviral drug by a single enzyme: adenosine deaminase catalyzes two consecutive deamination reactions
Abstract
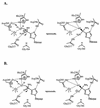
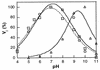
Ribavirin is an approved broad-spectrum antiviral drug. A liver-targeting prodrug of ribavirin, viramidine, is in clinical trial in an attempt to provide a better therapeutic index. The conversion of viramidine to ribavirin, and of ribavirin to an inactive metabolite through adenosine deaminase, is reported. Kinetic analysis indicates that adenosine deaminase is likely involved in activation of viramidine in vivo, and the process is highly pH sensitive. The differential activities of two consecutive deamination reactions are kinetically studied and interpreted based on adenosine deaminase structural information. A comprehensive understanding of the viramidine and ribavirin deamination mechanism should help in designing better nucleoside therapeutics in the future.
Figures

References
-
- Crotty, S., D. Maag, J. J. Arnold, W. Zhong, J. Y. Lau, Z. Hong, R. Andino, and C. E. Cameron. 2000. The broad-spectrum antiviral ribonucleoside ribavirin is an RNA virus mutagen. Nat. Med. 6:1375-1379. - PubMed
-
- Daddona, P. E., D. S. Shewach, W. N. Kelley, P. Argos, A. F. Markham, and S. H. Orkin. 1984. Human adenosine deaminase. cDNA and complete primary amino acid sequence J. Biol. Chem. 259:12101-12106. - PubMed
-
- Davis, G. L., R. Esteban-Mur, V. Rustgi, J. Hoefs, S. C. Gordon, C. Trepo, M. L. Shiffman, S. Zeuzem, A. Craxi, M. H. Ling, and J. Albrecht. 1998. Interferon alfa-2b alone or in combination with ribavirin for the treatment of relapse of chronic hepatitis C. N. Engl J. Med. 339:1493-1499. - PubMed
-
- Driscoll, J. S., M. A. Siddiqui, H. Ford, Jr., J. A. Kelley, J. S. Roth, H. Mitsuya, M. Tanaka, and V. E. Marquez. 1996. Lipophilic, acid-stable, adenosine deaminase-activated anti-HIV prodrugs for central nervous system delivery. 3. 6-Amino prodrugs of 2′-beta-fluoro-2′,3′-dideoxyinosine. J. Med. Chem. 39:1619-1625. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

