Medication adherence among HIV+ adults: effects of cognitive dysfunction and regimen complexity
- PMID: 12499488
- PMCID: PMC2871670
- DOI: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000038347.48137.67
Medication adherence among HIV+ adults: effects of cognitive dysfunction and regimen complexity
Abstract
Background: Although the use of highly active antiretroviral therapy in the treatment of HIV infection has led to considerable improvement in morbidity and mortality, unless patients are adherent to their drug regimen (i.e., at least 90 to 95% of doses taken), viral replication may ensue and drug-resistant strains of the virus may emerge.
Methods: The authors studied the extent to which neuropsychological compromise and medication regimen complexity are predictive of poor adherence in a convenience sample of 137 HIV-infected adults. Medication adherence was tracked through the use of electronic monitoring technology (MEMS caps).
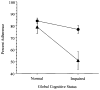
Results: Two-way analysis of variance revealed that neurocognitive compromise as well as complex medication regimens were associated with significantly lower adherence rates. Cognitively compromised participants on more complex regimens had the greatest difficulty with adherence. Deficits in executive function, memory, and attention were associated with poor adherence. Logistic regression analysis demonstrated that neuropsychological compromise was associated with a 2.3 times greater risk of adherence failure. Older age (>50 years) was also found to be associated with significantly better adherence.
Conclusions: HIV-infected adults with significant neurocognitive compromise are at risk for poor medication adherence, particularly if they have been prescribed a complex dosing regimen. As such, simpler dosing schedules for more cognitively impaired patients might improve adherence.
Figures
Comment in
-
Medication adherence among HIV+ adults: effects of cognitive dysfunction and regimen complexity.Neurology. 2003 Sep 9;61(5):723-4; author reply 724. doi: 10.1212/wnl.61.5.723. Neurology. 2003. PMID: 12963784 Clinical Trial. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hammer SM, Squires KE, Hughes MD, et al. A controlled trial of two nucleoside analogues plus indinavir in persons with human immunodeficiency virus infection and CD4 cell counts of 200 per cubic millimeter or less. AIDS Clinical Trials Group 320 Study Team. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:725–733. - PubMed
-
- Hogg RS, Heath KV, Yip B, et al. Improved survival among HIV-infected individuals following initiation of antiretroviral therapy. JAMA. 1998;279:450–454. - PubMed
-
- Montaner JS, Hogg R, Raboud J, Harrigan R, O’Shaughnessy M. Antiretroviral treatment in 1998. Lancet. 1998;352:1919–1922. - PubMed
-
- Palella FJ, Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, et al. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:853–860. - PubMed
-
- Ferrando S, van Gorp W, McElhiney M, Goggin K, Sewell M, Rabkin J. Highly active antiretroviral treatment in HIV infection: benefits for neuropsychological function. AIDS. 1998;12:F65–F70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous