An effective omentoplasty technique in laparoscopic surgery for hydatid disease of the liver
- PMID: 12500830
- PMCID: PMC3043437
An effective omentoplasty technique in laparoscopic surgery for hydatid disease of the liver
Abstract
Objectives: The objectives of this study were to investigate the characteristics and outcome of patients with hydatid disease of the liver who were laparoscopically managed at our clinic and to define technical details including an effective method of omentoplasty with helical fasteners.
Methods: Between January 1998 and November 2000, 13 patients, mean age 36 years (range 23 to 63 years), with hydatid disease of the liver were considered for laparoscopic surgery in our department. All the patients underwent laparoscopic surgical interventions.
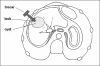
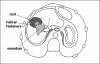
Results: In all patients, laparoscopic cystotomy, unroofing, and omentoplasty with helical fasteners, which were originally designed for endoscopic hernia repair procedures, were performed. No conversion to laparotomy was necessary. In 1 case, with a single cyst in the right lobe, bile leakage was observed. No radiological recurrence was observed in an average follow-up of 17 months (range 4 to 36 months).
Conclusions: Obliteration of the residual cystic cavity decreases postoperative complication rates, so an effective omentoplasty is essential especially for laparoscopic procedures. Laparoscopy is quite feasible to perform in hydatid disease of the liver, and the use of helical fasteners allows effective omental flap fixation.
Figures
References
-
- Ammann RW, Eckert J. Cestodes. Echinococcus. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1996;25:655–689 - PubMed
-
- King CH. Cestodes. In: Mandell GL, Benett JE, Dolin R. eds. Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 5th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Churchill Livingstone Inc; 2000:2957–2963
-
- Seven R, Berber E, Mercan S, Eminoglu L, Budak D. Laparoscopic treatment of hepatic hydatid cysts. Surgery. 2000;128:36–40 - PubMed
-
- Alper A, Emre A, Acarli K, Bilge O, Ozden I, Ariogul O. Laparoscopic treatment of hepatic hydatid disease. J Laparoendosc Surg. 1996;6:29–33 - PubMed
-
- Ertem M, Uras C, Karahasanoglu T, Erguney S, Alemdaroglu K. Laparoscopic approach to hepatic hydatid disease. Dig Surg. 1998;15:333–336 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources