A cytoskeleton-like role for the bacterial cell wall during engulfment of the Bacillus subtilis forespore
- PMID: 12502745
- PMCID: PMC187501
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1039902
A cytoskeleton-like role for the bacterial cell wall during engulfment of the Bacillus subtilis forespore
Abstract
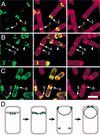
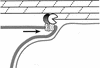
A hallmark of bacterial endospore formation is engulfment, during which the membrane of one cell (the mother cell) migrates around the future spore, enclosing it in the mother cell cytoplasm. Bacteria lack proteins required for eukaryotic phagocytosis, and previously proteins required for membrane migration remained unidentified. Here we provide cell biological and genetic evidence that three membrane proteins synthesized in the mother cell are required for membrane migration as well as for earlier steps in engulfment. Biochemical studies demonstrate that one of these proteins, SpoIID, is a cell wall hydrolase, suggesting that membrane migration in bacteria can be driven by membrane-anchored cell wall hydrolases. We propose that the bacterial cell wall plays a role analogous to that of the actin and tubulin network of eukaryotic cells, providing a scaffold along which proteins can move.
Figures



References
-
- Barrett JF, Dolinger DL, Schramm VL, Shockman GD. The mechanism of soluble peptidoglycan hydrolysis by an autolytic muramidase. A processive exodisaccharidase. J Biol Chem. 1984;259:11818–11827. - PubMed
-
- Blackman SA, Smith TJ, Foster SJ. The role of autolysins during vegetative growth of Bacillus subtilis 168. Microbiology. 1998;144:73–82. - PubMed
-
- Driks A, Roels S, Beall B, Moran CP, Jr, Losick R. Subcellular localization of proteins involved in the assembly of the spore coat of Bacillus subtilis. Genes & Dev. 1994;8:234–244. - PubMed
-
- Dubnau D, Davidoff-Abelson R. Fate of transforming DNA following uptake by competent Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1971;56:209–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
