Development of mice expressing a single D-type cyclin
- PMID: 12502747
- PMCID: PMC187507
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1023602
Development of mice expressing a single D-type cyclin
Abstract
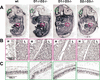
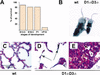
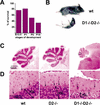
D-cyclins (cyclins D1, D2, and D3) are components of the core cell cycle machinery. To directly test the ability of each D-cyclin to drive development of various lineages, we generated mice expressing only cyclin D1, or only cyclin D2, or only cyclin D3. We found that these "single-cyclin" embryos develop normally until late gestation. Our analyses revealed that in single-cyclin embryos, the tissue-specific expression pattern of D-cyclins was lost. Instead, mutant embryos ubiquitously expressed the remaining D-cyclin. These findings suggest that the functions of the three D-cyclins are largely exchangeable at this stage. Later in life, single-cyclin mice displayed focused abnormalities, resulting in premature mortality. "Cyclin D1-only" mice developed severe megaloblastic anemia, "cyclin D2-only" mice presented neurological abnormalities, and "cyclin D3-only" mice lacked normal cerebella. Analyses of the affected tissues revealed that these compartments failed to sufficiently up-regulate the remaining, intact D-cyclin. In particular, we found that in cerebellar granule neuron precursors, the N-myc transcription factor communicates with the cell cycle machinery via cyclins D1 and D2, but not D3, explaining the inability of D3-only mice to up-regulate cyclin D3 in this compartment. Hence, the requirement for a particular cyclin in a given tissue is likely caused by specific transcription factors, rather than by unique properties of cyclins.
Figures





References
-
- Adams PD. Regulation of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein by cyclin/cdks. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001;1471:M123–M133. - PubMed
-
- Aguzzi A, Kiess M, Rued D, Hamel PA. Cyclins D1, D2 and D3 are expressed in distinct tissues during mouse embryogenesis. Transgenics. 1996;2:29–39.
-
- Altman J, Bayer SA. Development of cerebellar system in relation to its evolution, structure and functions. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 1997.
-
- Bartkova J, Lukas J, Strauss M, Bartek J. Cyclin D3: Requirement for G1/S transition and high abundance in quiescent tissues suggest a dual role in proliferation and differentiation. Oncogene. 1998;17:1027–1037. - PubMed
-
- Bates S, Bonetta L, MacAllan D, Parry D, Holder A, Dickson C, Peters G. CDK6 (PLSTIRE) and CDK4 (PSK-J3) are a distinct subset of the cyclin-dependent kinases that associate with cyclin D1. Oncogene. 1994;9:71–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
