Drosophila MUS312 interacts with the nucleotide excision repair endonuclease MEI-9 to generate meiotic crossovers
- PMID: 12504024
- PMCID: PMC3206640
- DOI: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00782-7
Drosophila MUS312 interacts with the nucleotide excision repair endonuclease MEI-9 to generate meiotic crossovers
Abstract
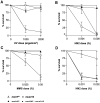
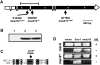
MEI-9 is the Drosophila homolog of the human structure-specific DNA endonuclease XPF. Like XPF, MEI-9 functions in nucleotide excision repair and interstrand crosslink repair. MEI-9 is also required to generate meiotic crossovers, in a function thought to be associated with resolution of Holliday junction intermediates. We report here the identification of MUS312, a protein that physically interacts with MEI-9. We show that mutations in mus312 elicit a meiotic phenotype identical to that of mei-9 mutants. A missense mutation in mei-9 that disrupts the MEI-9-MUS312 interaction abolishes the meiotic function of mei-9 but does not affect the DNA repair functions of mei-9. We propose that MUS312 facilitates resolution of meiotic Holliday junction intermediates by MEI-9.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Drosophila ERCC1 is required for a subset of MEI-9-dependent meiotic crossovers.Genetics. 2005 Aug;170(4):1737-45. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.036178. Epub 2005 Jun 8. Genetics. 2005. PMID: 15944364 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila hold'em is required for a subset of meiotic crossovers and interacts with the dna repair endonuclease complex subunits MEI-9 and ERCC1.Genetics. 2009 Jan;181(1):335-40. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.093104. Epub 2008 Oct 28. Genetics. 2009. PMID: 18957705 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila MUS312 and the vertebrate ortholog BTBD12 interact with DNA structure-specific endonucleases in DNA repair and recombination.Mol Cell. 2009 Jul 10;35(1):128-35. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.06.019. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19595722 Free PMC article.
-
Holliday junctions in the eukaryotic nucleus: resolution in sight?Trends Biochem Sci. 2003 Oct;28(10):548-57. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2003.08.011. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003. PMID: 14559184 Review.
-
Unique invasions and resolutions: DNA repair proteins in meiotic recombination in Drosophila melanogaster.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004;107(3-4):172-9. doi: 10.1159/000080595. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004. PMID: 15467362 Review.
Cited by
-
On the role of AtDMC1, AtRAD51 and its paralogs during Arabidopsis meiosis.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Feb 17;5:23. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00023. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24596572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammalian BTBD12/SLX4 assembles a Holliday junction resolvase and is required for DNA repair.Cell. 2009 Jul 10;138(1):63-77. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.06.030. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19596235 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial regulation of meiotic holliday junction resolution in C. elegans by HIM-6 (BLM) helicase, SLX-4, and the SLX-1, MUS-81 and XPF-1 nucleases.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(7):e1003591. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003591. Epub 2013 Jul 18. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23901331 Free PMC article.
-
A genetic screen for DNA double-strand break repair mutations in Drosophila.Genetics. 2007 Sep;177(1):63-77. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.077693. Epub 2007 Jul 29. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17660539 Free PMC article.
-
MUS81 generates a subset of MLH1-MLH3-independent crossovers in mammalian meiosis.PLoS Genet. 2008 Sep 12;4(9):e1000186. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000186. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18787696 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bardwell AJ, Bardwell L, Tomkinson AE, Friedberg EC. Specific cleavage of model recombination and repair intermediates by the yeast Rad1-Rad10 DNA endonuclease. Science. 1994;265:2082–2085. - PubMed
-
- Boddy MN, Gaillard PH, McDonald WH, Shanahan P, Yates JR, 3rd, Russell P. Mus81-Eme1 are essential components of a Holliday junction resolvase. Cell. 2001;107:537–548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

