Drosophila MUS312 interacts with the nucleotide excision repair endonuclease MEI-9 to generate meiotic crossovers
- PMID: 12504024
- PMCID: PMC3206640
- DOI: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00782-7
Drosophila MUS312 interacts with the nucleotide excision repair endonuclease MEI-9 to generate meiotic crossovers
Abstract
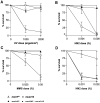
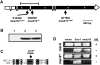
MEI-9 is the Drosophila homolog of the human structure-specific DNA endonuclease XPF. Like XPF, MEI-9 functions in nucleotide excision repair and interstrand crosslink repair. MEI-9 is also required to generate meiotic crossovers, in a function thought to be associated with resolution of Holliday junction intermediates. We report here the identification of MUS312, a protein that physically interacts with MEI-9. We show that mutations in mus312 elicit a meiotic phenotype identical to that of mei-9 mutants. A missense mutation in mei-9 that disrupts the MEI-9-MUS312 interaction abolishes the meiotic function of mei-9 but does not affect the DNA repair functions of mei-9. We propose that MUS312 facilitates resolution of meiotic Holliday junction intermediates by MEI-9.
Figures
References
-
- Bardwell AJ, Bardwell L, Tomkinson AE, Friedberg EC. Specific cleavage of model recombination and repair intermediates by the yeast Rad1-Rad10 DNA endonuclease. Science. 1994;265:2082–2085. - PubMed
-
- Boddy MN, Gaillard PH, McDonald WH, Shanahan P, Yates JR, 3rd, Russell P. Mus81-Eme1 are essential components of a Holliday junction resolvase. Cell. 2001;107:537–548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

