Cathepsin A regulates chaperone-mediated autophagy through cleavage of the lysosomal receptor
- PMID: 12505983
- PMCID: PMC140041
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg002
Cathepsin A regulates chaperone-mediated autophagy through cleavage of the lysosomal receptor
Abstract
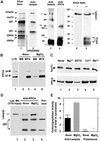
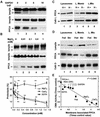
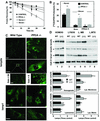
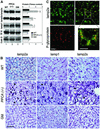
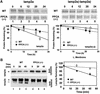
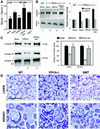
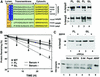
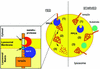
Protective protein/cathepsin A (PPCA) has a serine carboxypeptidase activity of unknown physiological function. We now demonstrate that this protease activity triggers the degradation of the lysosome-associated membrane protein type 2a (lamp2a), a receptor for chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA). Degradation of lamp2a is important because its level in the lysosomal membrane is a rate-limiting step of CMA. Cells defective in PPCA show reduced rates of lamp2a degradation, higher levels of lamp2a and higher rates of CMA. Restoration of PPCA protease activity increases rates of lamp2a degradation, reduces levels of lysosomal lamp2a and reduces rates of CMA. PPCA associates with lamp2a on the lysosomal membrane and cleaves lamp2a near the boundary between the luminal and transmembrane domains. In addition to the well-studied role of PPCA in targeting and protecting two lysosomal glycosidases, we have defined a role for the proteolytic activity of this multifunctional protein.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of lamp2a levels in the lysosomal membrane.Traffic. 2000 Jul;1(7):570-83. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2000.010707.x. Traffic. 2000. PMID: 11208145
-
Unique properties of lamp2a compared to other lamp2 isoforms.J Cell Sci. 2000 Dec;113 Pt 24:4441-50. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113.24.4441. J Cell Sci. 2000. PMID: 11082038
-
Lysosome membrane lipid microdomains: novel regulators of chaperone-mediated autophagy.EMBO J. 2006 Sep 6;25(17):3921-33. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601283. Epub 2006 Aug 17. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16917501 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of chaperone-mediated autophagy.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004 Dec;36(12):2435-44. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2004.02.013. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15325583 Review.
-
Chaperone-mediated autophagy.Autophagy. 2007 Jul-Aug;3(4):295-9. doi: 10.4161/auto.4144. Epub 2007 Jul 15. Autophagy. 2007. PMID: 17404494 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of chaperone-mediated autophagy during oxidative stress.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Nov;15(11):4829-40. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-06-0477. Epub 2004 Aug 25. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15331765 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing chaperone-mediated autophagy for the selective degradation of mutant huntingtin protein.Nat Biotechnol. 2010 Mar;28(3):256-63. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1608. Epub 2010 Feb 28. Nat Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20190739
-
Leptin Modulates the Metastasis of Canine Inflammatory Mammary Adenocarcinoma Cells Through Downregulation of Lysosomal Protective Protein Cathepsin A (CTSA).Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 25;21(23):8963. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238963. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33255835 Free PMC article.
-
Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy Reactivation Protects Against Severe Acute Pancreatitis-Associated Liver Injury Through Upregulating Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway and Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Feb 25. doi: 10.1007/s12013-025-01677-7. Online ahead of print. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39998716
-
Chaperone-mediated autophagy: selectivity pays off.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Mar;21(3):142-50. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2009.10.003. Epub 2009 Oct 24. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 19857975 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akiyama T., Kihara,A., Tokuda,H. and Ito,K. (1996) FtsH (HflB) is an ATP-dependent protease selectively acting on SecY and some other membrane proteins. J. Biol. Chem., 271, 31196–31201. - PubMed
-
- Auteri J.S. et al. (1983) Regulation of intracellular protein degradation in IMR-90 human diploid fibroblasts. J. Cell Physiol., 115, 159–166. - PubMed
-
- Bonten E.J., Galjart,N.J., Willemsen,R., Usmany,M., Vlak,J.M. and d’Azzo,A. (1995) Lysosomal protective protein/cathepsin A. Role of the ‘linker’ domain in catalytic activation. J. Biol. Chem., 270, 26441–26445. - PubMed
-
- Chiang H.L., Terlecky,S.R., Plant,C.P. and Dice,J.F. (1989) A role for a 70-kilodalton heat shock protein in lysosomal degradation of intracellular proteins. Science, 246, 382–385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

