Pseudomonas type III effector AvrPtoB induces plant disease susceptibility by inhibition of host programmed cell death
- PMID: 12505984
- PMCID: PMC140047
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg006
Pseudomonas type III effector AvrPtoB induces plant disease susceptibility by inhibition of host programmed cell death
Abstract
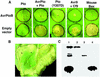
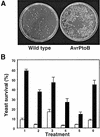
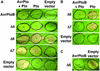
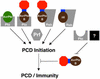
The AvrPtoB type III effector protein is conserved among diverse genera of plant pathogens suggesting it plays an important role in pathogenesis. Here we report that Pseudomonas AvrPtoB acts inside the plant cell to inhibit programmed cell death (PCD) initiated by the Pto and Cf9 disease resistance proteins and, remarkably, the pro-apoptotic mouse protein Bax. AvrPtoB also suppressed PCD in yeast, demonstrating that AvrPtoB functions as a cell death inhibitor across kingdoms. Using truncated AvrPtoB proteins, we identified distinct N- and C-terminal domains of AvrPtoB that are sufficient for host recognition and PCD inhibition, respectively. We also identified a novel resistance phenotype, Rsb, that is triggered by an AvrPtoB truncation disrupted in the anti-PCD domain. A Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 strain with a chromosomal mutation in the AvrPtoB C-terminus elicited Rsb-mediated immunity in previously susceptible tomato plants and disease was restored when full-length AvrPtoB was expressed in trans. Thus, our results indicate that a type III effector can induce plant susceptibility to bacterial infection by inhibiting host PCD.
Figures




References
-
- Aoyama T. and Chua,N.-H. (1997) A glucocorticoid-mediated transcrip tional induction system in transgenic plants. Plant J., 11, 605–612. - PubMed
-
- Boch J., Joardar,V., Gao,L., Robertson,T.L., Lim,M. and Kunkel,B.N. (2002) Identification of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato genes induced during infection of Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Microbiol., 44, 73–88. - PubMed
-
- Chang J.H., Rathjen,J.P., Bernal,A.J., Staskawicz,B.J. and Michelmore,R.W. (2000) avrPto enhances growth and necrosis caused by Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato in tomato lines lacking either Pto or Prf. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact., 13, 568–571. - PubMed
-
- Chen Z., Kloek,A.P., Boch,J., Katagiri,F. and Kunkel,B.N. (2000) The Pseudomonas syringae avrRpt2 gene product promotes pathogen virulence from inside plant cells. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact., 13, 1312–1321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

