Engrailed cooperates with extradenticle and homothorax to repress target genes in Drosophila
- PMID: 12506004
- PMCID: PMC2692026
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.00289
Engrailed cooperates with extradenticle and homothorax to repress target genes in Drosophila
Abstract
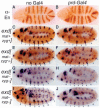
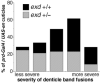
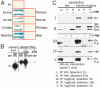
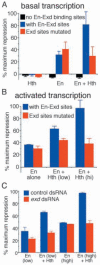
Engrailed is a key transcriptional regulator in the nervous system and in the maintenance of developmental boundaries in Drosophila, and its vertebrate homologs regulate brain and limb development. Here, we show that the functions of both of the Hox cofactors Extradenticle and Homothorax play essential roles in repression by Engrailed. Mutations that remove either of them abrogate the ability of Engrailed to repress its target genes in embryos, both cofactors interact directly with Engrailed, and both stimulate repression by Engrailed in cultured cells. We suggest a model in which Engrailed, Extradenticle and Homothorax function as a complex to repress Engrailed target genes. These studies expand the functional requirements for extradenticle and homothorax beyond the Hox proteins to a larger family of non-Hox homeodomain proteins.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Engrailed cooperates directly with Extradenticle and Homothorax on a distinct class of homeodomain binding sites to repress sloppy paired.Dev Biol. 2012 Jun 15;366(2):382-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.04.004. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22537495 Free PMC article.
-
Requirements for transcriptional repression and activation by Engrailed in Drosophila embryos.Development. 2003 Feb;130(4):729-39. doi: 10.1242/dev.00286. Development. 2003. PMID: 12506003
-
Hox repression of a target gene: extradenticle-independent, additive action through multiple monomer binding sites.Development. 2002 Jul;129(13):3115-26. doi: 10.1242/dev.129.13.3115. Development. 2002. PMID: 12070087
-
Conserved roles of engrailed: patterning tissues and specifying cell types.Development. 2024 Dec 15;151(24):dev204250. doi: 10.1242/dev.204250. Epub 2024 Dec 13. Development. 2024. PMID: 39671171 Review.
-
Antennapedia: The complexity of a master developmental transcription factor.Genesis. 2024 Feb;62(1):e23561. doi: 10.1002/dvg.23561. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Genesis. 2024. PMID: 37830148 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution of an insect-specific GROUCHO-interaction motif in the ENGRAILED selector protein.Evol Dev. 2008 Sep-Oct;10(5):537-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-142X.2008.00269.x. Evol Dev. 2008. PMID: 18803772 Free PMC article.
-
Engrailed cooperates directly with Extradenticle and Homothorax on a distinct class of homeodomain binding sites to repress sloppy paired.Dev Biol. 2012 Jun 15;366(2):382-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.04.004. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22537495 Free PMC article.
-
Pbx homeodomain proteins: TALEnted regulators of limb patterning and outgrowth.Dev Dyn. 2011 May;240(5):1063-86. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22605. Epub 2011 Mar 17. Dev Dyn. 2011. PMID: 21416555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homothorax controls a binary Rhodopsin switch in Drosophila ocelli.PLoS Genet. 2021 Jul 27;17(7):e1009460. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009460. eCollection 2021 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34314427 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptome analyses of the Drosophila pupal eye.G3 (Bethesda). 2021 Jan 18;11(1):jkaa003. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkaa003. G3 (Bethesda). 2021. PMID: 33561221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abu-Shaar M, Mann RS. Generation of multiple antagonistic domains along the proximodistal axis during Drosophila leg development. Development. 1998;125:3821–3830. - PubMed
-
- Abzhanov A, Holtzman S, Kaufman TC. The Drosophila proboscis is specified by two Hox genes, proboscipedia and Sex combs reduced, via repression of leg and antennal appendage genes. Development. 2001;128:2803–2814. - PubMed
-
- Akam M. The molecular basis for metameric pattern in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1987;101:1–22. - PubMed
-
- Alexandre C, Vincent J-P. Requirements for transcriptional repression and activation by Engrailed in Drosophila embryos. Development. 2003;130:729–739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

