Chronic repetitive reaching and grasping results in decreased motor performance and widespread tissue responses in a rat model of MSD
- PMID: 12507595
- PMCID: PMC1560095
- DOI: 10.1016/S0736-0266(02)00086-4
Chronic repetitive reaching and grasping results in decreased motor performance and widespread tissue responses in a rat model of MSD
Abstract
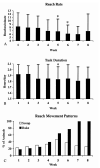
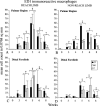
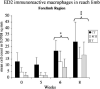
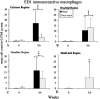
This study investigated changes in motor skills and tissues of the upper extremity (UE) with regard to injury and inflammatory reactions resulting from performance of a voluntary forelimb repetitive reaching and grasping task in rats. Rats reached for food at a rate of 4 reaches/min, 2 h/day, and 3 days/week for up to 8 weeks during which reach rate, task duration and movement strategies were observed. UE tissues were collected bilaterally at weekly time points of 3-8 weeks and examined for morphological changes. Serum was tested for levels of interleukin-1alpha (IL-1) protein. The macrophage-specific antibody, ED1, was used to identify infiltrating macrophages and the ED2 antibody was used to identify resident macrophages. Rats were unable to maintain baseline reach rate in weeks 5 and 6 of task performance. Alternative patterns of movement emerged. Fraying of tendon fibrils was observed after 6 weeks in the mid-forelimb. After 4 weeks, a general elevation of ED1-IR macrophages were seen in all tissues examined bilaterally including the contralateral, uninvolved forelimb and hindlimbs. Significantly more resident macrophages were seen at 6 and 8 weeks in the reach limb. At 8 weeks, serum levels of IL-1alpha increased significantly above week 0. Our results demonstrate that performance of repetitive tasks elicits motor decrements, signs of injury and a cellular and tissue responses associated with inflammation.
Figures

References
-
- Almekinders LC, Banes AJ, Ballenger CA. Effects of repetitive motion on human fibroblasts. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1993;25(5):603–7. - PubMed
-
- Archambault JM, Herzog W, Hart D. The effect of load history in an experimental model of tendon repetitive motion disorders. Proceedings of the Marconi Research Conference Marshall; CA. 1997.
-
- Armstrong RB, Ogilvie RW, Schwane JA. Eccentric exercise-induced injury to rat skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol. 1983;54:80–93. - PubMed
-
- Barr AE, Safadi FF, Garvin RP, Popoff SN, Barbe MF. Evidence of progressive tissue pathophysiology and motor behavior degradation in a rat model of work related musculoskeletal disease. Proceedings of the IEA 2000/HFES 2000 Congress. 2000;5:584–7.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

