Primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma: high frequency of BCL-6 mutations and consistent expression of the transcription factors OCT-2, BOB.1, and PU.1 in the absence of immunoglobulins
- PMID: 12507907
- PMCID: PMC1851125
- DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63815-1
Primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma: high frequency of BCL-6 mutations and consistent expression of the transcription factors OCT-2, BOB.1, and PU.1 in the absence of immunoglobulins
Abstract
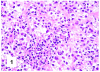
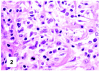
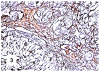
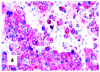
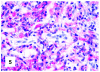
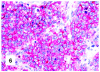
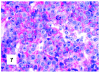
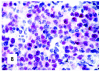
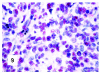
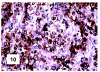
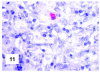
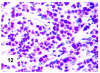
Although primary mediastinal (thymic) large B-cell lymphoma has been primarily studied, its precise phenotype, molecular characteristics, and histogenesis are still a matter of debate. The International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group collected 137 such cases for extensive pathological review. Histologically, the lymphomatous growth was predominantly diffuse with fibrosis that induced compartmentalized cell aggregation. It consisted of large cells with varying degrees of nuclear polymorphism and clear to basophilic cytoplasm. On immunohistochemistry, the following phenotype was observed: CD45(+), CD20(+), CD79a(+), PAX5/BSAP(+), BOB.1(+), Oct-2(+), PU.1(+), Bcl-2(+), CD30(+), HLA-DR(+), MAL protein(+/-), Bcl-6(+/-), MUM1/IRF4(+/-), CD10(-/+), CD21(-), CD15(-), CD138(-), CD68(-), and CD3(-). Immunoglobulins were negative both at immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization. Molecular analysis, performed in 45 cases, showed novel findings. More than half of the cases displayed BCL-6 gene mutations, which usually occurred along with functioning somatic IgV(H) gene mutations and Bcl-6 and/or MUM1/IRF4 expression. The present study supports the concept that a sizable fraction of cases of this lymphoma are from activated germinal center or postgerminal center cells. However, it differs from other aggressive B-cell lymphomas in that it shows defective immunoglobulin production despite the expression of OCT-2, BOB.1, and PU.1 transcription factors and the lack of IgV(H) gene crippling mutations.
Figures
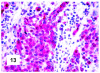
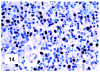
References
-
- Lichtenstein A, Levine A, Taylor CR, Boswell W, Rossamn S, Feinstein DI, Lukes RJ: Primary mediastinal lymphoma in adults. Am J Med 1980, 68:509-514 - PubMed
-
- Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Stein H, Banks PM, Chan JK, Cleary ML, Delsol G, De Wolf-Peeters C, Falini B, Gatter KC: A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: a proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood 1994, 84:1316-1392 - PubMed
-
- Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW: Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Jaffe ES Harris NL Stein H Vardiman MJ eds. 2001:pp 175-176 IARC Press, Lyon
-
- Addis BJ, Isaacson PG: Large cell lymphoma of the mediastinum: a B-cell tumor of probable thymic origin. Histopathology 1986, 10:379-390 - PubMed
-
- Menestrina F, Chilosi M, Bonetti F, Lestani M, Scarpa A, Novelli P, Doglioni C, Todeschini G, Ambrosetti A, Fiore-Donati L: Mediastinal large-cell lymphoma of B-type, with sclerosis: histopathological and immunohistochemical study of eight cases. Histopathology 1986, 10:589-600 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

