Tissue-specific inactivation of murine M6P/IGF2R
- PMID: 12507915
- PMCID: PMC1851115
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63823-0
Tissue-specific inactivation of murine M6P/IGF2R
Abstract
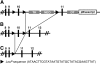
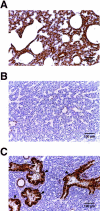
The mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor (M6P/IGF2R) encodes a multifunctional protein involved in lysosomal enzyme trafficking, fetal organogenesis, tumor suppression, and T cell- mediated immunity. M6P/IGF2R is an imprinted gene in mice with expression only from the maternal allele. Complete knockout of this gene causes neonatal lethality, thus preventing analysis of its multifunctional role postnatally. To help elucidate the biological functions of M6P/IGF2R in adulthood, we generated both complete and tissue-specific M6P/IGF2R knockout mice using the Cre/loxP system. We confirm that complete M6P/IGF2R knockout results in fetal overgrowth and neonatal lethality. In contrast, tissue-specific inactivation of this gene in either the liver or skeletal and cardiac muscle gives rise to viable animals with no obvious phenotype. The successful creation of viable tissue-specific M6P/IGF2R knockout mouse models will now allow for detailed analysis of receptor function in a number of cellular processes including brain development, carcinogenesis, lysosomal trafficking, and T cell-mediated immunity.
Figures


Comment in
-
Keys to the hidden treasures of the mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor.Am J Pathol. 2003 Jan;162(1):3-6. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63791-1. Am J Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12507883 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kornfeld S: Structure and function of the mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor II receptors. Annu Rev Biochem 1992, 61:307-330 - PubMed
-
- Jirtle RL: Mannose 6-phosphate receptors. Creidton TE eds. Encyclopedia of Molecular Biology. 1999, :pp 1441-1447 Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York
-
- Morgan DO, Edman JC, Standring DN, Fried VA, Smith MC, Roth RA, Rutter WJ: Insulin-like growth factor II receptor as a multifunctional binding protein. Nature 1987, 329:301-307 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

