Null mutation of DNA strand break-binding molecule poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase causes medulloblastomas in p53(-/-) mice
- PMID: 12507917
- PMCID: PMC1851106
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63825-4
Null mutation of DNA strand break-binding molecule poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase causes medulloblastomas in p53(-/-) mice
Abstract
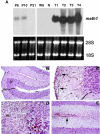
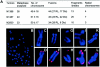
Medulloblastoma is an invasive embryonal tumor of the cerebellum with predominant neuronal differentiation. Although several genes have been implicated in medulloblasoma formation, such as Patched (Ptc1) and the adenomatous polyposis coli gene (Apc), the majority of these tumors cannot be explained by mutations in these genes. The cellular origin as well as the genetic and molecular changes involved in the genesis and progression of human medulloblastomas remain largely unknown. Here we show that disruption of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP-1) causes a high incidence (49%) of aggressive brain tumors in p53 null mice, with typical features of human cerebellar medulloblastomas. At as early as 8 weeks of age, lesions started on the outer surface of the cerebellum from remnant granule cell precursors of the developmental external germinal layer. Progression of these tumors is associated with the re-activation of the neuronal specific transcription factor Math1, dysregulation of Shh/Ptc1 signaling pathway, and chromosomal aberrations, including triradial and quadriradial chromosomes. The present study indicates that the loss of function of DNA double-strand break-sensing and repair molecules is an etiological factor in the evolution of the cerebellar medulloblastomas. These PARP-1/p53 double null mice represent a novel model for the pathogenesis of human medulloblastomas.
Figures



Comment in
-
Medulloblastoma in mice lacking p53 and PARP: all roads lead to Gli.Am J Pathol. 2003 Jan;162(1):7-10. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63792-3. Am J Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12507884 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Medulloblastoma in mice lacking p53 and PARP: all roads lead to Gli.Am J Pathol. 2003 Jan;162(1):7-10. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63792-3. Am J Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12507884 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
PARP-1 cooperates with Ptc1 to suppress medulloblastoma and basal cell carcinoma.Carcinogenesis. 2008 Oct;29(10):1911-9. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgn174. Epub 2008 Jul 27. Carcinogenesis. 2008. PMID: 18660545
-
The normal patched allele is expressed in medulloblastomas from mice with heterozygous germ-line mutation of patched.Cancer Res. 2000 Apr 15;60(8):2239-46. Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10786690
-
Cerebellum Development and Tumorigenesis: A p53-Centric Perspective.Trends Mol Med. 2016 May;22(5):404-413. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2016.03.006. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Trends Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27085812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A mouse model for medulloblastoma and basal cell nevus syndrome.J Neurooncol. 2001 Jul;53(3):307-18. doi: 10.1023/a:1012260318979. J Neurooncol. 2001. PMID: 11718263 Review.
Cited by
-
Math1 target genes are enriched with evolutionarily conserved clustered E-box binding sites.J Mol Neurosci. 2006;28(2):211-29. doi: 10.1385/JMN:28:2:211. J Mol Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16679559
-
The Machado-Joseph Disease Deubiquitinase Ataxin-3 Regulates the Stability and Apoptotic Function of p53.PLoS Biol. 2016 Nov 16;14(11):e2000733. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2000733. eCollection 2016 Nov. PLoS Biol. 2016. PMID: 27851749 Free PMC article.
-
A distinct response to endogenous DNA damage in the development of Nbs1-deficient cortical neurons.Cell Res. 2012 May;22(5):859-72. doi: 10.1038/cr.2012.3. Epub 2012 Jan 3. Cell Res. 2012. PMID: 22212482 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Notch and Wnt pathway components and activation of Notch signaling in medulloblastomas from heterozygous patched mice.J Neurooncol. 2006 Sep;79(3):221-7. doi: 10.1007/s11060-006-9132-2. Epub 2006 Apr 6. J Neurooncol. 2006. PMID: 16598417
-
Multifaceted Role of PARP-1 in DNA Repair and Inflammation: Pathological and Therapeutic Implications in Cancer and Non-Cancer Diseases.Cells. 2019 Dec 22;9(1):41. doi: 10.3390/cells9010041. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31877876 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kleihues P, Cavenee WK: World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. Pathology and Genetics: Tumours of the Nervous System. 2000:pp 129-137 IARC Press, Lyon
-
- Lantos PL, Louis DN, Rosenblum MK, Kleihues P: Greenfield’s Neuropathology ed 7 2002:pp 117-132 Arnold, London
-
- Malkin D: The Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Vogelstein B Kinzler KW eds. The Genetic Basis of Human Cancer. 1998:pp 393-407 McGraw-Hill, New York
-
- Hahn H, Wicking C, Zaphiropoulous PG, Gailani MR, Shanley S, Chidambaram A, Vorechovsky I, Holmberg E, Unden AB, Gillies S, Negus K, Smyth I, Pressman C, Leffell DJ, Gerrard B, Goldstein AM, Dean M, Toftgard R, Chenevix-Trench G, Wainwright B, Bale AE: Mutations of the human homolog of Drosophila patched in the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Cell 1996, 85:841-851 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

