Growth suppression of pre-T acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells by inhibition of notch signaling
- PMID: 12509463
- PMCID: PMC151540
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.2.655-664.2003
Growth suppression of pre-T acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells by inhibition of notch signaling
Abstract
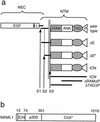
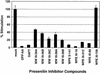
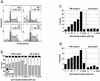
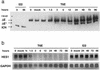
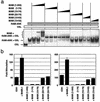
Constitutive NOTCH signaling in lymphoid progenitors promotes the development of immature T-cell lymphoblastic neoplasms (T-ALLs). Although it is clear that Notch signaling can initiate leukemogenesis, it has not previously been established whether continued NOTCH signaling is required to maintain T-ALL growth. We demonstrate here that the blockade of Notch signaling at two independent steps suppresses the growth and survival of NOTCH1-transformed T-ALL cells. First, inhibitors of presenilin specifically induce growth suppression and apoptosis of a murine T-ALL cell line that requires presenilin-dependent proteolysis of the Notch receptor in order for its intracellular domain to translocate to the nucleus. Second, a 62-amino-acid peptide derived from a NOTCH coactivator, Mastermind-like-1 (MAML1), forms a transcriptionally inert nuclear complex with NOTCH1 and CSL and specifically inhibits the growth of both murine and human NOTCH1-transformed T-ALLs. These studies show that continued growth and survival of NOTCH1-transformed lymphoid cell lines require nuclear access and transcriptional coactivator recruitment by NOTCH1 and identify at least two steps in the Notch signaling pathway as potential targets for chemotherapeutic intervention.
Figures
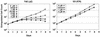


References
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas, S., M. D. Rand, and R. J. Lake. 1999. Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science 284:770-776. - PubMed
-
- Aster, J., W. Pear, R. Hasserjian, H. Erba, F. Davi, B. Luo, M. Scott, D. Baltimore, and J. Sklar. 1994. Functional analysis of the TAN-1 gene, a human homolog of Drosophila notch. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 59:125-136. - PubMed
-
- Aster, J. C., E. S. Robertson, R. P. Hasserjian, J. R. Turner, E. Kieff, and J. Sklar. 1997. Oncogenic forms of NOTCH1 lacking either the primary binding site for RBP-Jκ or nuclear localization sequences retain the ability to associate with RBP-Jκ and activate transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 272:11336-11343. - PubMed
-
- Berezovska, O., C. Jack, P. McLean, J. C. Aster, C. Hicks, W. Xia, M. S. Wolfe, W. T. Kimberly, G. Weinmaster, D. J. Selkoe, and B. T. Hyman. 2000. Aspartate mutations in presenilin and gamma-secretase inhibitors both impair notch1 proteolysis and nuclear translocation with relative preservation of notch1 signaling. J. Neurochem. 75:583-593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
