Flagella and Motility in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae
- PMID: 12511514
- PMCID: PMC145319
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.2.664-668.2003
Flagella and Motility in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae
Abstract
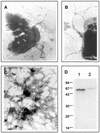
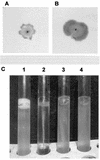
Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae has been considered nonmotile and nonflagellate. In this work, it is demonstrated that A. pleuropneumoniae produces flagella composed of a 65-kDa protein with an N-terminal amino acid sequence that shows 100% identity with those of Escherichia coli, Salmonella, and Shigella flagellins. The DNA sequence obtained through PCR of the fliC gene in A. pleuropneumoniae showed considerable identity (93%) in its 5' and 3' ends with the DNA sequences of corresponding genes in E. coli, Salmonella enterica, and Shigella spp. The motility of A. pleuropneumoniae was observed in tryptic soy or brain heart infusion soft agar media, and it is influenced by temperature. Flagella and motility may be involved in the survival and pathogenesis of A. pleuropneumoniae in pigs.
Figures

References
-
- Akerley, B. J., P. A. Cotter, and J. F. Miller. 1995. Ectopic expression of the flagellar regulon alters development of Bordetella-host interactions. Cell 80:611-620. - PubMed
-
- Bradford, M. M. 1968. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principles of protein dye-binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

