Termination of translation: interplay of mRNA, rRNAs and release factors?
- PMID: 12514123
- PMCID: PMC140092
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg017
Termination of translation: interplay of mRNA, rRNAs and release factors?
Abstract
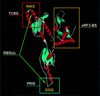
Termination of translation in eukaryotes has focused recently on functional anatomy of polypeptide chain release factor, eRF1, by using a variety of different approaches. The tight correlation between the domain structure and different functions of eRF1 has been revealed. Independently, the role of prokaryotic RF1/2 in GTPase activity of RF3 has been deciphered, as well as RF3 function itself.
Figures

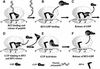
References
-
- Arkov A.L. and Murgola,J. (1999) Ribosomal RNAs in translation termination: facts and hypotheses. Biochimiya (Moscow), 64, 1354–1359. - PubMed
-
- Bertram G., Innes,S., Minella,O., Richardson.J. and Stansfield,I. (2001) Endless possibilities: translation termination and stop codon recognition. Microbiology, 147, 255–269. - PubMed
-
- Buckingham R.H., Grentzmann,G. and Kisselev,L. (1997) Polypeptide chain release factors. Mol. Microbiol., 24, 449–456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

