Mechanism of histone lysine methyl transfer revealed by the structure of SET7/9-AdoMet
- PMID: 12514135
- PMCID: PMC140100
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg025
Mechanism of histone lysine methyl transfer revealed by the structure of SET7/9-AdoMet
Abstract
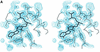
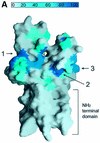
The methylation of lysine residues of histones plays a pivotal role in the regulation of chromatin structure and gene expression. Here, we report two crystal structures of SET7/9, a histone methyltransferase (HMTase) that transfers methyl groups to Lys4 of histone H3, in complex with S-adenosyl-L-methionine (AdoMet) determined at 1.7 and 2.3 A resolution. The structures reveal an active site consisting of: (i) a binding pocket between the SET domain and a c-SET helix where an AdoMet molecule in an unusual conformation binds; (ii) a narrow substrate-specific channel that only unmethylated lysine residues can access; and (iii) a catalytic tyrosine residue. The methyl group of AdoMet is directed to the narrow channel where a substrate lysine enters from the opposite side. We demonstrate that SET7/9 can transfer two but not three methyl groups to unmodified Lys4 of H3 without substrate dissociation. The unusual features of the SET domain-containing HMTase discriminate between the un- and methylated lysine substrate, and the methylation sites for the histone H3 tail.
Figures








References
-
- Bannister A.J., Zegerman,P., Partridge,J.F., Miska,E.A., Thomas,J.O., Allshire,R.C. and Kouzarides,T. (2001) Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature, 410, 120–124. - PubMed
-
- Boggs B.A., Cheung,P., Heard,E., Spector,D.L., Chinault,A.C. and Allis,C.D. (2002) Differentially methylated forms of histone H3 show unique association patterns with inactive human X chromosomes. Nat. Genet., 30, 73–76. - PubMed
-
- Brünger A.T. et al. (1998) Crystallography and NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D, 54, 905–921. - PubMed
-
- Byvoet P., Shepherd,G.R., Hardin,J.M. and Noland,B.J. (1972) The distribution and turnover of labeled methyl groups in histone fractions of cultured mammalian cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 148, 558–567. - PubMed
-
- CCP4 (1994) The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D, 50, 760–763. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

