Novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease by peripheral administration of agents with an affinity to beta-amyloid
- PMID: 12514198
- PMCID: PMC6742136
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-01-00029.2003
Novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease by peripheral administration of agents with an affinity to beta-amyloid
Abstract
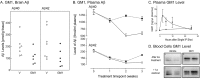
Plaques containing beta-amyloid (Abeta) peptides are one of the pathological features of Alzheimer's disease, and the reduction of Abeta is considered a primary therapeutic target. Amyloid clearance by anti-Abeta antibodies has been reported after immunization, and recent data have shown that the antibodies may act as a peripheral sink for Abeta, thus altering the periphery/brain dynamics. Here we show that peripheral treatment with an agent that has high affinity for Abeta (gelsolin or GM1) but that is unrelated to an antibody or immune modulator reduced the level of Abeta in the brain, most likely because of a peripherally acting effect. We propose that in general, compounds that sequester plasma Abeta could reduce or prevent brain amyloidosis, which would enable the development of new therapeutic agents that are not limited by the need to penetrate the brain or evoke an immune response.
Figures

References
-
- Bard F, Cannon C, Barbour R, Burke RL, Games D, Grajeda H, Guido T, Hu K, Huang J, Johnson-Wood K, Khan K, Kholodenko D, Lee M, Lieberburg I, Motter R, Nguyen M, Soriano F, Vasquez N, Weiss K, Welch B. Peripherally administered antibodies against amyloid β-peptide enter the central nervous system and reduce pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Nat Med. 2000;6:916–919. - PubMed
-
- Calhoun ME, Burgermeister P, Phinney AL, Stalder M, Tolnay M, Wiederhold KH, Abramowski D, Sturchler-Pierrat C, Sommer B, Staufenbiel M, Jucker M. Neuronal overexpression of mutant amyloid precursor protein results in prominent deposition of cerebrovascular amyloid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:14088–14093. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chauhan VP, Ray I, Chauhan A, Wisniewski HM. Binding of gelsolin, a secretory protein, to amyloid β-protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;258:241–246. - PubMed
-
- Choo-Smith LP, Garzon-Rodriguez W, Glabe CG, Surewicz WK. Acceleration of amyloid fibril formation by specific binding of Aβ-(1–40) peptide to anglioside-containing membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:22987–22990. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
