Addition of the keto functional group to the genetic code of Escherichia coli
- PMID: 12518054
- PMCID: PMC140882
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0234824100
Addition of the keto functional group to the genetic code of Escherichia coli
Abstract
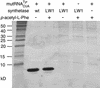
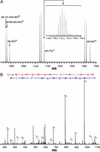
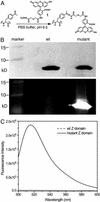
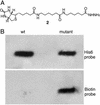
Although the keto group is the most versatile of the functional groups in organic chemistry, it is absent in the genetically encoded amino acids. To overcome this natural limitation on protein biosynthesis, we have evolved an orthogonal tRNA-synthetase pair that makes possible the efficient incorporation of a keto amino acid, p-acetyl-l-phenylalanine, into proteins in E. coli with high translational fidelity in response to the amber nonsense codon. To demonstrate the utility of this keto amino acid, we have used it to modify a protein selectively with a small molecule fluorophore and biotin derivative. This additional genetically encoded amino acid should greatly expand our ability to manipulate protein structure and function both in vitro and in living cells.
Figures
References
-
- Bock A, Forchhammer K, Heider J, Leinfelder W, Sawers G, Veprek B, Zinoni F. Mol Microbiol. 1991;5:515–520. - PubMed
-
- Srinivasan G, James C M, Krzycki J A. Science. 2002;296:1459–1462. - PubMed
-
- Hao B, Gong W, Ferguson T K, James C M, Krzycki J A, Chan M K. Science. 2002;296:1462–1466. - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Brock A, Herberich B, Schultz P G. Science. 2001;292:498–500. - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Brock A, Schultz P G. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124:1836–1837. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

