Dorsal penile nerve stimulation elicits left-hemisphere dominant activation in the second somatosensory cortex
- PMID: 12518289
- PMCID: PMC6871929
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.10078
Dorsal penile nerve stimulation elicits left-hemisphere dominant activation in the second somatosensory cortex
Abstract
Activation of peripheral mixed and cutaneous nerves activates a distributed cortical network including the second somatosensory cortex (SII) in the parietal operculum. SII activation has not been previously reported in the stimulation of the dorsal penile nerve (DPN). We recorded somatosensory evoked fields (SEFs) to DPN stimulation from 7 healthy adults with a 122-channel whole-scalp neuromagnetometer. Electrical pulses were applied once every 0.5 or 1.5 sec to the left and right DPN. For comparison, left and right median and tibial nerves were stimulated alternatingly at 1.5-sec intervals. DPN stimuli elicited weak, early responses in the vicinity of responses to tibial nerve stimulation in the primary somatosensory cortex. Strong later responses, peaking at 107-126 msec were evoked in the SII cortices of both hemispheres, with left-hemisphere dominance. In addition to tactile processing, SII could also contribute to mediating emotional effects of DPN stimuli.
Copyright 2002 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
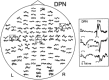
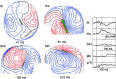

References
-
- Ahonen A, Hämäläinen M, Kajola M, Knuutila J, Laine P, Lounasmaa O, Parkkonen L, Simola J, Tesche C (1993): 122‐channel SQUID instrument for investigating the magnetic signals from human brain. Phys Scripta T49: 198–205.
-
- Alary F, Simoes C, Jousmäki V, Forss N, Hari R (2002): Cortical activity associated with passive movements of human index finger: a MEG study. NeuroImage 15: 691–696. - PubMed
-
- Allison T, McCarthy G, Wood C, Williamson P, Spencer D (1989): Human cortical potentials evoked by stimulation of the median nerve. II. Cytoarchitechtonic areas generating long‐latency activation. J Neurophysiol 62: 711–722. - PubMed
-
- Allison T, McCarthy G, Luby M, Puce A, Spencer D (1996): Localization of functional regions of human mesial cortex by somatosensory evoked potential recording and by cortical stimulation. Electroenceph Clin Neurophysiol 100: 126–140. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

