Plasma exchange for myasthenia gravis
- PMID: 12519572
- PMCID: PMC8985203
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002275
Plasma exchange for myasthenia gravis
Abstract
Background: Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease mediated by auto-antibodies direct against the nicotinic receptor for acetylcholine. Patients would be expected to benefit from plasma exchange. Non-randomised studies suggest that plasma exchange is beneficial in the short term.
Objectives: To examine the efficacy of plasma exchange in the short and long term treatment of myasthenia gravis.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Neuromuscular Disease Group register (searched 17 July 2002) and MEDLINE (January 1966 to June 2002) for randomised controlled trials using myasthenia gravis as the search term. We checked the bibliographies in reports of randomised trials and contacted one author to identify additional published or unpublished data.
Selection criteria: Types of studies: All randomised or quasi-randomised studies.
Types of participants: All patients with myasthenia gravis who were diagnosed by an internationally accepted definition. Types of intervention: Treatment with plasma exchange alone or combined with steroids or immunosuppressive drugs. Types of outcome measures:
Primary outcome measure: ~bullet~patients treated for exacerbation: change in a specific muscle score after plasma exchange; ~bullet~patients treated for chronic myasthenia gravis: change in a functional scale.
Secondary outcome measures: ~bullet~patients treated for exacerbation: change in a functional scale and percentage weaned from mechanical ventilation; ~bullet~patients treated for chronic myasthenia gravis: percentage in remission by the end of one year after first plasma exchange; ~bullet~adverse events.
Data collection and analysis: One author extracted the data and the two others checked them. Since there was only one trial no formal meta-analysis was required.
Main results: We identified one randomised controlled trial. Improvement in a quantitative muscle score was not significantly greater in patients treated with plasma exchange and prednisone than in patients treated with prednisone alone one month after onset of treatment. More relapses were observed in the plasma exchange and prednisone group in the first year as compared with the prednisone alone group. Problems in recruitment and matching of patients entered into this trial limit the conclusions that can be drawn. On the other hand,experience from many non-randomised studies suggests that plasma exchange is beneficial in myasthenia gravis. Consequently the relative benefits of plasma exchange are still unconfirmed.
Reviewer's conclusions: There are no adequate randomised controlled trials but many case series report short-term benefit from plasma exchange in myasthenia gravis, especially in myasthenic crisis. There are no adequate randomised controlled trials to determine whether plasma exchange improves the long-term outcome for myasthenia gravis. Further research is need to compare plasma exchange with alternative short-term treatments for myasthenic crisis and to determine the value of long-term plasma exchange for treating myasthenia gravis.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures

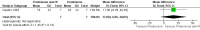
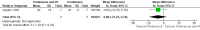

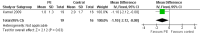






References
References to studies included in this review
Gajdos 1983 {published data only}
-
- Gajdos P, Simon N, Rohan‐Chabot P, Raphaël JC, Goulon M. Long term effects of plasma exchange in myasthenia. Results from a randomized study [Effet à long terme des échanges plasmatiques au cours de la myasthénie. Résultat d'une étude randomisée]. Presse Médicale 1983;12(15):939‐42. [PUBMED: 6221247] - PubMed
Gajdos 1997 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Gajdos P, Chevret S, Clair B, Tranchant C, Chastang C. Clinical trial of plasma exchange and high‐dose immunoglobulin in myasthenia gravis. Myasthenia Gravis Clinical Study Group. Annals of Neurology 1997;41(6):789‐96. [PUBMED: 9189040] - PubMed
Kamel 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kamel A, Essa M. Effectiveness of prethymecthomy plasmapheresis on short‐term outcome of non‐thymomatous generalized myasthenia gravis. Egyptian Journal Neurology, Psychiatry and Neurosurgurgery 2009;46(1):161‐8.
Ronager 2001 {published data only}
-
- Rønager J, Ravnborg M, Hermansen I, Vorstrup S. Immunoglobulin treatment versus plasma exchange in patients with chronic moderate to severe myasthenia gravis. Artificial Organs 2001;25(12):967‐73. [PUBMED: 11843764] - PubMed
Additional references
AAN 1996
-
- Assessment of plasmapheresis. Report of the therapeutics and technology assessment subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 1996;47(3):840‐3. - PubMed
Antozzi 1991
-
- Antozzi C, Gemma M, Regi B, Berta E, Confalonieri P, Peluchetti D, et al. A short plasma exchange protocol is effective in severe myasthenia gravis. Journal of Neurology 1991;238(2):103‐7. - PubMed
Behan 1979
-
- Behan PO, Shakir RA, Simpson JA, Burnett AK, Allan TL, Haase G. Plasma‐exchange combined with immunosuppressive therapy in myasthenia gravis. Lancet 1979;2(8140):438‐40. - PubMed
Bergamini 1983
-
- Bergamini L, Cocito D, Durelli L, Quattrocolo G. Opinions about plasma exchange and associated treatments in the therapy of myasthenia gravis. Muscle and Nerve 1983;6(6):457‐8. - PubMed
Besinger 1983
-
- Besinger UA, Toyka KV, Hömberg M, Heininger K, Hohlfeld R, Fateh‐Moghadam A. Myasthenia gravis: long‐term correlation of binding and bungarotoxin blocking antibodies against acetylcholine receptors with changes in disease severity. Neurology 1983;33(10):1316‐21. - PubMed
Chiu 2000
-
- Chiu HC, Chen WH, Yeh JH. The six year experience of plasmapheresis in patients with myasthenia gravis. Therapeutic Apheresis: official journal of the International Society for Apheresis and the Japanese Society for Apheresis 2000;4(4):291‐5. - PubMed
Cole 2008
-
- Cole RN, Reddel SW, Gervasio OL, Phillips WD. Anti‐MuSK patient antibodies disrupt the mouse neuromuscular junction.. Ann Neurol 2008;63(6):782‐9. - PubMed
Cornelio 1993
-
- Cornelio F, Antozzi C, Mantegazza R, Confalonieri P, Berta E, Peluchetti D, et al. Immunosuppressive treatments. Their efficacy on myasthenia gravis patients' outcome and on the natural course of the disease. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1993;681:594‐602. - PubMed
D'Empaire 1985
-
- d'Empaire G, Hoaglin DC, Perlo VP, Pontoppidan H. Effect of prethymecthomy plasma exchange on postoperative respiratory function in myasthenia gravis. Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery 1985;89(4):592‐596. - PubMed
Dau 1977
-
- Dau PC, Lindstrom JM, Cassel CK, Denys EH, Shev EE, Spitler LE. Plasmapheresis and immunosuppressive drug therapy in myasthenia gravis. New England Journal of Medicine 1977;297(21):1134‐40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dau 1979
-
- Dau PC. Plasmapheresis and the immunology of myasthenia gravis. Boston: Hougton‐Mifflin, 1979.
Dau 1980
-
- Dau PC. Plasmapheresis therapy in myasthenia gravis. Muscle and Nerve 1980;3(6):468‐82. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dau 1981
-
- Dau PC. Response to plasmapheresis and immunosuppressive drug therapy in sixty myasthenia gravis patients. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1981;377:700‐8. - PubMed
Fornasari 1985
-
- Fornasari PM, Riva G, Piccolo G, Cosi V, Lombardi M. Short and long‐term clinical effects of plasma exchange in 33 cases of myasthenia gravis. The International Journal of Artificial Organs 1985;8(3):159‐62. - PubMed
Gajdos 2003a
Gajdos 2003b
-
- Gajdos P, Shashar T, Chevret S. Standards of measurements in myasthenia gravis. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2003;998:445‐52. - PubMed
Grob 1981
-
- Grob D, Brunner NG, Namba T. The natural course of myasthenia gravis and effect of therapeutic measures. Annals of the New York Academy of Science 1981;377(1):652‐69. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Heininger 1987
-
- Heininger K, Hartung HP, Toyka KV, Gaczkowski A, Borberg H. Therapeutic plasma exchange in myasthenia gravis: semiselective adsorption of anti‐AChR autoantibodies with tryptophane linked polyvinyalcohol gels. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1987;505:898‐900.
Higgins 2008
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, 2008.
Hohlfeld 1993
-
- Hohlfeld R, Toyka KV. Therapies. In: Baets MH, Oosterhuis H editor(s). Myasthenia Gravis. CRC Press, 1993:236‐57.
Hohlfeld 1996
-
- Hohlfeld R, Melms A, Toyka KV, Drachman DB. Therapy for myasthenia gravis and myasthenic syndromes. Neurological disorders: course and treatment. Academic Press, 1996.
Jaretzki 2000
-
- Jaretzki A, Barohn RJ, Ernstoff RM, Kaminski HJ, Keesey JC, Penn AS, et al. Myasthenia gravis. Recommendations for clinical research standards. Neurology 2000;55(1):16‐23. - PubMed
Jensen 2008
-
- Jensen P, Bril V. A comparison of the effectiveness of intravenous immunoglobulin and plasma exchange as preoperative therapy of myasthenia gravis. Journal of Clinical Neuromuscular Disease 2008;9(3):352‐5. - PubMed
Kornfeld 1979
-
- Kornfeld P, Ambinder EP, Papatestas AE, Bender AN, Genkins G. Plasmapheresis in myasthenia gravis: controlled study. Lancet 1979;2(8143):629. - PubMed
Kornfeld 1981
-
- Kornfeld P, Ambinder EP, Mittag T, Bender AN, Papatestas AE, Goldberg J, et al. Plasmapheresis in refractory generalized myasthenia gravis. Archives of Neurology 1981;38(8):478‐81. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mantegazza 1987
-
- Mantegazza R, Bruzzone E, Regi B, Peluchetti D, Marconi M, Sirchia G, et al. Single donor plasma in therapeutic exchange for myasthenia gravis. International Journal of Artificial Organs 1987;10(5):315‐8. - PubMed
Miller 1981
-
- Miller RG, Milner‐Brown HS, Dau PC. Antibody‐negative acquired myasthenia gravis. Successful therapy with plasma exchange (letter). Muscle and Nerve 1981;4(3):255. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Newsom‐Davis 1979
-
- Newsom‐Davis J, Wilson SG, Vincent A, Ward CD. Long‐term effects of repeated plasma exchange in myasthenia gravis. Lancet 1979;1(8114):464‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
NIH Consensus 1986
-
- NIH Consensus Conference. The utility of therapeutic plasmapheresis for neurological disorders. NIH Consensus Development.. Journal of the American Medical Association 1986;256(10):1333‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Olarte 1981
-
- Olarte MR, Schoenfeldt RS, Penn AS, Lovelace RE, Rowland LP. Effect of plasmapheresis in myasthenia gravis 1978‐1980. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1981;377:725‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Oosterhuis 1997
-
- Oosterhuis HJGH. Myasthenia gravis. Groningen: Groningen Neurological Press, 1997.
Patrick 1973
-
- Patrick J, Lindstrom J. Autoimmune response to acetylcholine receptor. Science 1973;180(88):871‐2. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Perez‐Nellar 2001
-
- Perez‐Nellar J, Dominguez AM, Llorens‐Figueroa JA, Ferra‐Betancourt A, Pardo A, Quiala M, et al. A comparative study of intravenous immunoglobulin and plasmapheresis preoperatively in myasthenia [Estudio comparativo entre immunoglobulina intravenosa y plasmaferesis en el perioperatorio de la miastenia gravis]. Revista de Neurologia 2001;33(5):413‐6. - PubMed
Perlo 1981
-
- Perlo VP, Shahani BT, Huggins CE, Hunt J, Kosinski K, Potts F. Effect of plasmapheresis in myasthenia gravis. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1981;377:709‐24. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pinching 1976
-
- Pinching AS, Peters DK. Remission of myasthenia gravis following plasma exchange. Lancet 1976;2(8000):1373‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Qureshi 1999
-
- Qureshi AI, Choudhry MA, Akbar MS, Mohammad Y, Chua HC, Yahia AM, et al. Plasma exchange versus intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in myasthenic crisis. Neurology 1999;52(3):629‐32. - PubMed
RevMan 2008 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008.
Richman 1980
-
- Richman DP, Gomez CM, Berman PW, Burres SA, Fitch FW, Arnason BG. Monoclonal anti acetylcholine receptor antibodies can cause experimental myasthenia. Nature 1980;286(5774):738‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rodnitzky 1984
-
- Rodnitzky RL, Bosch EP. Chronic long‐interval plasma exchange in myasthenia gravis. Archives of Neurology 1984;41(7):715‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Toyka 1975
-
- Toyka KV, Drachman DB, Pestronk A, Kao I. Myasthenia gravis: passive transfer from man to mouse. Science 1975;190(4212):397‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Vincent 2001
-
- Vincent A, Palace J, Hilton‐Jones D. Myasthenia gravis. Lancet 2001;357(9274):2122‐8. - PubMed
Yeh 1999
-
- Yeh JH, Chiu HC. Plasmapheresis in myasthenia gravis. A comparative study of daily versus alternately daily schedule. Acta Neurologica Scandanavica 1999;99(3):147‐51. - PubMed
Yeh 2000
-
- Yeh JH, Chiu HC. Comparison between double‐filtration plasmapheresis and immunoadsorption plasmapheresis in the treatment of patients with myasthenia gravis. Journal of Neurology 2000;247(7):510‐3. - PubMed
Yeh 2005
-
- Yeh JH, Chen WH, Huang KM, Chiu HC. Prethymecthomy plasmapheresis in myasthenia gravis. Journal of Clinical Apheresis 2005;20(4):217‐221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

