Effect of multiple freeze-thaw cycles on detection of measles, mumps, and rubella virus antibodies
- PMID: 12522034
- PMCID: PMC145292
- DOI: 10.1128/cdli.10.1.19-21.2003
Effect of multiple freeze-thaw cycles on detection of measles, mumps, and rubella virus antibodies
Abstract
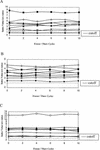
We investigated the effect of multiple freeze-thaw cycles on mumps, measles, and rubella virus serum antibody levels with whole-virus immunoglobulin G enzyme-linked immunoassays. Fresh serum samples from nine healthy adult volunteers were divided into six sets of five aliquots each. Samples were taken through a total of 10 freeze-thaw cycles and stored at 4 degrees C until assayed. Each assay measurement was done in replicates of five, and the mean value was reported. After completing 10 freeze-thaw cycles, we found no clinically or statistically significant effect on measured antibody levels and found no discernible detrimental effect on the ability to measure these antibodies by enzyme-linked immunoassays.
Figures
References
-
- Blincoe, C., and D. W. Marble. 1985. Storage stability of some bovine plasma enzymes. Am. J. Vet. Res. 46:1242-1244. - PubMed
-
- DiMagno, E. P., D. Corle, J. F. O'Brien, I. J. Masnyk, and R. Aamodt. 1989. Effect of long-term freezer storage, thawing, and refreezing on selected constituents of serum. Mayo Clin. Proc. 64:1226-1234. - PubMed
-
- Palombo, J. D., B. R. Bistrian, and G. L. Blackburn. 1987. Radioimmunoassay of apolipoprotein A-1 in serum and EDTA plasma, and effects of freeze-thaw cycles. Clin. Chem. 33:308. - PubMed
-
- Paul, J. R., and C. White. (ed.). 1973. Serologic epidemiology. Academic Press, New York, N.Y.
-
- Petrakis, N. L. 1985. Biologic banking in cohort studies, with special reference to blood. NCI Monogr. 67:193-198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

