Serum interferon (IFN)-neutralizing antibodies and bioactivities of IFNs in patients with severe type II essential mixed cryoglobulinemia
- PMID: 12522042
- PMCID: PMC145266
- DOI: 10.1128/cdli.10.1.70-77.2003
Serum interferon (IFN)-neutralizing antibodies and bioactivities of IFNs in patients with severe type II essential mixed cryoglobulinemia
Abstract
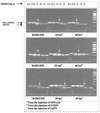
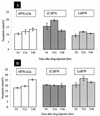
The efficacy of alpha interferon (IFN-alpha) in the treatment of severe type II essential mixed cryoglobulinemia (EMC) has been reported previously. In some patients, the development of neutralizing antibodies to recombinant IFN-alpha (rIFN-alpha) can affect the clinical response achieved with rIFN-alpha; a second treatment with natural IFN-alpha preparations may reinduce the clinical response. In the present study the ability of leukocyte IFN (LeIFN) to restore the response was investigated from a pharmacodynamic viewpoint. Specifically, the pharmacodynamic profiles of different IFN-alpha preparations were studied by measuring the serum neopterin levels and the levels of expression of protein MxA mRNA in in vivo peripheral blood mononuclear cells in two patients with EMC whose resistance to rIFN-alpha2a treatment increased concomitantly with the development of neutralizing antibodies. These markers were measured before injection and at 24 and 48 h after a single injection of rIFN-alpha2a, consensus IFN [(C)IFN], or LeIFN. No increase or only a slight increase in MxA mRNA levels was detectable after administration of rIFN-alpha2a or (C)IFN, whereas a significant increase (>/=10-fold) in MxA mRNA expression was recorded following administration of LeIFN. The neutralizing antibodies to rIFN-alpha2a cross-react with (C)IFN. Sera from these patients neutralized most but not all of the subtypes present in the natural IFN-alpha (LeIFN) mixture, and no significant increase in neopterin levels was observed after these patients were switched to LeIFN treatment. In summary, the data demonstrate that the problem of neutralizing antibodies still exists and that LeIFN may induce an increase in the level of MxA mRNA expression but not an increase in neopterin levels in patients who are resistant to treatment with rIFN-alpha2a or (C)IFN.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Resistance to recombinant alpha interferon therapy in idiopathic mixed cryoglobulinemia: reinduction of remission by natural alpha interferon both in antibody-positive and -negative patients.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 1994 Apr-Jun;8(2):56-9. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 1994. PMID: 7863814
-
Interferon-alpha neutralizing antibodies in HIV and chronic HCV patients treated with natural-source human leukocyte-derived interferon-alpha n3.Hum Antibodies. 1997;8(3):129-36. Hum Antibodies. 1997. PMID: 9322083
-
Rapid and simple detection of IFN-neutralizing antibodies in chronic hepatitis C non-responsive to IFN-alpha.J Med Virol. 2006 Jan;78(1):74-82. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20506. J Med Virol. 2006. PMID: 16299717
-
Antibodies to interferon-alpha in treated cancer patients: incidence and significance.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1997 Mar;17(3):141-3. doi: 10.1089/jir.1997.17.141. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1997. PMID: 9085938 Review.
-
[Alpha interferon, antiviral proteins and their value in clinical medicine].Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 1999 Nov-Dec;57(6):659-66. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 1999. PMID: 10572214 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Autologous albumin enhances the humoral immune response to capsular polysaccharide covalently coattached to bacteria-sized latex beads.Eur J Immunol. 2014 May;44(5):1433-43. doi: 10.1002/eji.201344266. Epub 2014 Feb 27. Eur J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24481921 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct Immunologic Properties of Soluble Versus Particulate Antigens.Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 21;9:598. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00598. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29619034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of biomarkers of interferon type I in patients suffering from chronic diseases.Clin Exp Immunol. 2007 Feb;147(2):270-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03280.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17223968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antonelli, G. 1997. In vivo development of antibody to interferons: an update to 1996. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 17:S39-S46. - PubMed
-
- Antonelli, G., F. Bagnato, C. Pozzilli, E. Simeoni, S. Bastianelli, M. Currenti, F. De Pisa, C. Fieschi, C. Gasperini, M. Salvetti, and F. Dianzani. 1998. Development of neutralizing antibodies in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis treated with IFN-β1a. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 18:345-350. - PubMed
-
- Antonelli, G., E. Simeoni, O. Turriziani, R. Tesoro, A. Redaelli, L. Roffi, L. Antonelli, M. Pistello, and F. Dianzani. 1999. Correlation of interferon-induced expression of MxA mRNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells with the response of patients with chronic active hepatitis C to IFN-α therapy. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 19:243-251. - PubMed
-
- Berg, T., U. Hopf, and P. Schuff-Werner. 2001. Sustained remission of chronic hepatitis C after a change to human leukocyte interferon-alpha in a difficult-to-treat patient with breakthrough phenomenon associated with antibodies against recombinant interferon-alpha. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 96:612-614. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

