Specificity and diversity of antibodies to Mycobacterium tuberculosis arabinomannan
- PMID: 12522045
- PMCID: PMC145285
- DOI: 10.1128/cdli.10.1.88-94.2003
Specificity and diversity of antibodies to Mycobacterium tuberculosis arabinomannan
Abstract
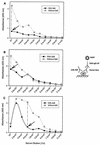
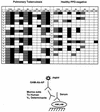
Arabinomannan (AM) is a polysaccharide antigen of the mycobacterial capsule. However, it is uncertain whether AM constitutes an immunologically distinct fraction of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In this study, we analyzed the repertoire and specificity of antibodies to AM by using AM-binding murine monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) and human serum samples. Murine MAbs were found to be diverse in their specificity to AM and cross-reactivity with other arabinose-containing mycobacterial polysaccharides, with MAb 9d8 binding exclusively to AM. Human antibodies to AM were detected in serum samples from patients with pulmonary tuberculosis (TB), as well as in those from healthy, purified protein derivative-negative controls, with significantly higher titers among patients. The binding of human antibodies to AM was inhibited by MAb 9d8 in three patients with TB but not in controls. MAb 5c11, which recognizes other mycobacterial arabinose-containing carbohydrates in addition to AM, inhibited the binding of serum samples from 75% of patients and 76% of controls. Analysis of human antibodies with murine MAbs to human V(H) determinants demonstrated diversity among antibodies to AM with qualitative and quantitative differences compared with antibodies to lipoarabinomannan. In summary, our study suggests that antibodies to AM are diverse and heterogeneous with respect to antigen recognition and V(H) determinant expression, with human serum samples containing different subsets of antibodies to AM with the specificities of AM-binding murine MAbs. One MAb and a subset of human antibodies bind AM specifically, suggesting that this polysaccharide is antigenically distinct and is expressed in human infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Human Antibodies to Arabinomannan With Enhanced Mycobacterial Opsonophagocytosis and Intracellular Growth Reduction.J Infect Dis. 2016 Jul 15;214(2):300-10. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw141. Epub 2016 Apr 7. J Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27056953 Free PMC article.
-
Antigenic evidence of prevalence and diversity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis arabinomannan.J Clin Microbiol. 2004 Jul;42(7):3225-31. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.7.3225-3231.2004. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15243086 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of a Mycobacterium tuberculosis arabinomannan antigen in vitro and in vivo.Infect Immun. 2001 Sep;69(9):5671-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.9.5671-5678.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11500443 Free PMC article.
-
Monoclonal antibodies to lipoarabinomannan/arabinomannan - characteristics and implications for tuberculosis research and diagnostics.Trends Microbiol. 2023 Jan;31(1):22-35. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2022.07.001. Epub 2022 Jul 30. Trends Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 35918247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Mycobacterium tuberculosis capsule: a cell structure with key implications in pathogenesis.Biochem J. 2019 Jul 18;476(14):1995-2016. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20190324. Biochem J. 2019. PMID: 31320388 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Determination of variable region sequences from hybridoma immunoglobulins that target Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence factors.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 20;16(8):e0256079. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256079. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34415957 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis extrapulmonary dissemination in mice by an arabinomannan-protein conjugate vaccine.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Mar 9;13(3):e1006250. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006250. eCollection 2017 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28278283 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced virulence of Histoplasma capsulatum through transfer and surface incorporation of glycans from Cryptococcus neoformans during co-infection.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 24;6:21765. doi: 10.1038/srep21765. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26908077 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Human Antibodies to Arabinomannan With Enhanced Mycobacterial Opsonophagocytosis and Intracellular Growth Reduction.J Infect Dis. 2016 Jul 15;214(2):300-10. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw141. Epub 2016 Apr 7. J Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27056953 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative evaluation of profiles of antibodies to mycobacterial capsular polysaccharides in tuberculosis patients and controls stratified by HIV status.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012 Feb;19(2):198-208. doi: 10.1128/CVI.05550-11. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22169090 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abadi, J., J. Friedman, R. A. Mageed, R. Jefferis, M. C. Rodriguez-Barradas, and L. Pirofski. 1998. Human antibodies elicited by a pneumococcal vaccine express idiotypic determinants indicative of VH3 gene segment usage. J. Infect. Dis. 178:707-716. - PubMed
-
- Adderson, E. E., P. G. Shackelford, A. Quinn, P. M. Wilson, M. W. Cunningham, R. A. Insel, and W. L. Carroll. 1993. Restricted immunoglobulin VH usage and VDJ combinations in the human response to Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide. Nucleotide sequences of monospecific anti-Haemophilus antibodies and polyspecific antibodies cross-reacting with self antigens. J. Clin. Investig. 91:2734-2743. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bridges, A., A. Birch, G. Williams, M. Aguet, D. Schlatter, W. Huber, G. Garotta, and J. A. Robinson. 1995. Variable region cDNA sequences and characterization of murine anti-human interferon gamma receptor monoclonal antibodies that inhibit receptor binding by interferon gamma. Mol. Immunol. 32:1329-1338. - PubMed
-
- Brown, J. C., B. A. Brown II, Y. Li, and C. C. Hardin. 1998. Construction and characterization of a quadruplex DNA selective single-chain autoantibody from a viable moth-eaten mouse hybridoma with homology to telomeric DNA binding proteins. Biochemistry 37:16338-16348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- AI053192/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033142/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI044374/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033774/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI045459/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059842/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI044374/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI035370/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI033142/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI033774/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AI053192/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL059842/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI001691/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI033142/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI001691/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI035370/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI045459/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

