Simultaneous detection of 15 human cytokines in a single sample of stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- PMID: 12522051
- PMCID: PMC145264
- DOI: 10.1128/cdli.10.1.133-139.2003
Simultaneous detection of 15 human cytokines in a single sample of stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells
Abstract
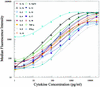
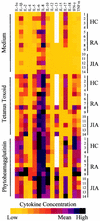
Cytokines secreted by cells of the immune system can alter the behavior and properties of immune or other cells. At a site of inflammation, sets of cytokines interact with immune cells, and their combined effect is often more important than the function of one isolated component. Conventional techniques, such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, generally require large quantities of cells to characterize a complete cytokine profile of activated lymphocytes. The Bio-Plex system from Bio-Rad Laboratories combines the principle of a sandwich immunoassay with the Luminex fluorescent-bead-based technology. We developed a multiplex cytokine assay to detect different cytokines simultaneously in culture supernatant of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells stimulated with antigen and with mitogen. Fifteen human cytokines (interleukin 1alpha [IL-1alpha], IL-1beta, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12p70, IL-13, IL-15, IL-17, IL-18, gamma interferon, and tumor necrosis factor alpha) were validated with a panel of healthy individuals, rheumatoid arthritis patients, and juvenile idiopathic arthritis patients. Comparing the multiplex assay with a regular enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technique with this donor panel resulted in correlation coefficients for all cytokines ranging from 0.75 to 0.99. Intra-assay variance proved to be less then 10%, whereas interassay variability ranged between 10 and 22%. This multiplex system proved to be a powerful tool in the quantitation of cytokines. It will provide a more complete picture in differences between activated lymphocyte cytokine profiles from healthy individuals and those from patients with chronic inflammatory diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Carson, R. T., and D. A. Vignali. 1999. Simultaneous quantitation of 15 cytokines using a multiplexed flow cytometric assay. J. Immunol. Methods 227:41-52. - PubMed
-
- Cook, E. B., J. L. Stahl, L. Lowe, R. Chen, E. Morgan, J. Wilson, R. Varro, A. Chan, F. M. Graziano, and N. P. Barney. 2001. Simultaneous measurement of six cytokines in a single sample of human tears using microparticle-based flow cytometry: allergics vs. non-allergics. J. Immunol. Methods 254:109-118. - PubMed
-
- Fulton, R. J., R. L. McDade, P. L. Smith, L. J. Kienker, and J. R. Kettman, Jr. 1997. Advanced multiplexed analysis with the FlowMetrix system. Clin. Chem. 43:1749-1756. - PubMed
-
- Gordon, R. F., and R. L. McDade. 1997. Multiplexed quantification of human IgG, IgA, and IgM with the FlowMetrix system. Clin. Chem. 43:1799-1801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

