Shaker-type Kv1 channel blockers increase the peristaltic activity of guinea-pig ileum by stimulating acetylcholine and tachykinins release by the enteric nervous system
- PMID: 12522073
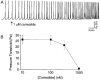
- PMCID: PMC1573649
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705023
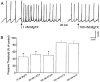
Shaker-type Kv1 channel blockers increase the peristaltic activity of guinea-pig ileum by stimulating acetylcholine and tachykinins release by the enteric nervous system
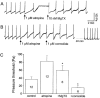
Abstract
1 A constant intraluminal pressure system was used to evaluate the effects of Kv1 channel blockers on the peristaltic activity of guinea-pig ileum. 2 The nortriterpene correolide, a non-selective inhibitor of all Kv1 sub-types, causes progressive and sustained reduction of the pressure threshold for eliciting peristaltic contractions. 3 Margatoxin (MgTX), alpha-dendrotoxin (alpha-DTX) and dendrotoxin-K (DTX-K), highly selective peptidyl inhibitors of certain Kv1 sub-types, cause immediate reduction of the pressure threshold. This effect subsides with time, irrespective of the peptides' concentration in the bath. In preparations pretreated with saturating concentrations of MgTX, correolide further stimulates the peristaltic activity. 4 Iberiotoxin (IbTX), a selective inhibitor of the high-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) (BK) channels, and charybdotoxin (ChTX), which inhibits Kv1.2 and Kv1.3 as well as BK channels, fail to stimulate the peristaltic activity. 5 Blockade of muscarinic receptors by atropine reduces, and occasionally suppresses the peristaltic activity of guinea-pig ileum. In atropine-treated preparations, correolide and MgTX retain their abilities to reduce the pressure threshold and are able to restore the peristaltic reflex in the preparations where this reflex was suppressed by atropine. 6 The stimulatory effect of correolide and MgTX in atropine-treated preparations is abolished by subsequent addition of selective antagonists of both NK1 and NK2 receptors. 7 In conclusion, blockade of Kv1, particularly Kv1.1 channels, increases the peristaltic activity of guinea-pig ileum by enhancing the release of neurotransmitters at the enteric nervous system. In contrast, stimulation of the myogenic motility by blockade of BK channels does not affect the threshold for the peristaltic reflex.
Figures
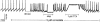

References
-
- BARTHÓ L., HOLZER P. The inhibitory modulation of guinea-pig intestinal peristalsis caused by capsaicin involves calcitonin gene-related peptide and nitric oxide. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 1995;353:102–109. - PubMed
-
- DE FARIAS F., CARVALHO M.F., LEE S.H., KACZOROWSKI G.J., SUAREZ-KURTZ G. Effects of the maxi-K channel blockers paspalitrem-C and paxilline on mammalian smooth muscle. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996;314:123–128. - PubMed
-
- FELIX J.P., BUGIANESI R.M., SCHMALHOFER W.A., BORRIS R., GOETZ M.A., HENSENS J.-M.B., KAYSER F., PARSONS W.H., RUPPRECHT K., GARCIA M.L., KACZOROWSKI G.J., SLAUGHTER R.S. Identification and biochemical characterization of a novel nortriterpene inhibitor of the voltage-gated potassium channel, Kv1.3. Biochemistry. 1999;38:4922–4930. - PubMed
-
- FURNESS J.B., COSTA M. The enteric nervous system. Edinburgh, U.K.: Churchill Livingstone; 1987.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

