Activation and potentiation of the NO/cGMP pathway by NG-hydroxyl-L-arginine in rabbit corpus cavernosum under normoxic and hypoxic conditions and ageing
- PMID: 12522074
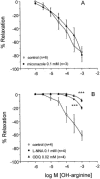
- PMCID: PMC1573653
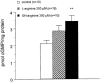
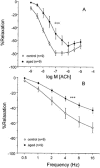
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705027
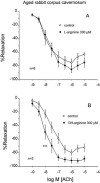
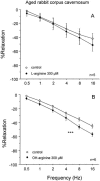
Activation and potentiation of the NO/cGMP pathway by NG-hydroxyl-L-arginine in rabbit corpus cavernosum under normoxic and hypoxic conditions and ageing
Abstract
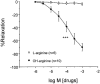
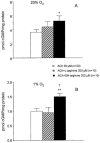
1 When nitric oxide synthase (NOS) produces NO from N(G)-hydroxy-L-arginine (OH-arginine) instead of L-arginine, the total requirement of molecular oxygen and NADPH to form NO is reduced. The aim of this work was to evaluate the effects of OH-arginine on the contractility of rabbit corpus cavernosum (RCC) and to compare the capacities of L-arginine and OH-arginine to enhance NO-mediated responses under normoxic and hypoxic conditions and in ageing, as models of defective NO production. 2 OH-arginine, but not L-arginine, was able to relax phenylephrine-contracted rabbit trabecular smooth muscle. OH-arginine-induced relaxation was inhibited by the NOS-inhibitor, L-NNA (300 microM), and by the guanylyl cyclase inhibitor, ODQ (20 microM), while it was not affected by the cytochrome P450 oxygenase inhibitor, miconazole (0.1 mM). Administration of OH-arginine, but not L-arginine, produced a significant increment of cGMP accumulation in RCC tissue. 3 Relaxation elicited by OH-arginine (300 microM) was still observed at low oxygen tension. The increase of cGMP levels induced by ACh (30 microM) in RCC was significantly enhanced by addition of OH-arginine (300 microM) in normoxic conditions, as well as under hypoxia, while L-arginine did not alter the effects of ACh on cGMP accumulation. 4 Endothelium-dependent and nitrergic nerve-mediated relaxations were both significantly reduced in RCC from aged animals (>20-months-old) when compared with young adult rabbits (5-months-old). Treatment with OH-arginine (300 microM) significantly potentiated endothelium-dependent and neurogenic relaxation in corpus cavernosum from aged rabbits, while L-arginine (300 microM) did not have significant effects. 5 Results show that OH-arginine promotes NO-mediated relaxation of RCC and potentiates the NO-mediated responses induced by stimulation of endogenous NO generation in hypoxic and aged tissues. We propose that the use of OH-arginine could be of interest in the treatment of erectile dysfunction, at least in those secondary to defective NO production.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of Tityus serrulatus scorpion venom on the rabbit isolated corpus cavernosum and the involvement of NANC nitrergic nerve fibres.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Feb;123(3):435-42. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701623. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9504384 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative effects of sildenafil, phentolamine, yohimbine and L-arginine on the rabbit corpus cavernosum.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2004 Apr;18(2):187-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2003.00229.x. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15066133
-
A nitric oxide-like factor mediates nonadrenergic-noncholinergic neurogenic relaxation of penile corpus cavernosum smooth muscle.J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):112-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI115266. J Clin Invest. 1991. PMID: 1647413 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide and depolarization induce hydroxyl radical generation.Jpn J Pharmacol. 2002 Jan;88(1):1-5. doi: 10.1254/jjp.88.1. Jpn J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11855667 Review.
-
The Effectiveness of L-arginine in Clinical Conditions Associated with Hypoxia.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 3;24(9):8205. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098205. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175912 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of urinary metabolites with potential blood pressure-lowering effects in lentil-fed spontaneously hypertensive rats.Eur J Nutr. 2018 Feb;57(1):297-308. doi: 10.1007/s00394-016-1319-5. Epub 2016 Oct 21. Eur J Nutr. 2018. PMID: 27770189
-
Therapy of erectile dysfunction: potential future treatments.Endocrine. 2004 Mar-Apr;23(2-3):167-76. doi: 10.1385/ENDO:23:2-3:167. Endocrine. 2004. PMID: 15146097 Review.
-
Animal models of erectile dysfunction.Indian J Urol. 2015 Jan-Mar;31(1):15-21. doi: 10.4103/0970-1591.128496. Indian J Urol. 2015. PMID: 25624570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erectile dysfunction in a murine model of sleep apnea.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008 Sep 15;178(6):644-50. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200801-190OC. Epub 2008 Jun 5. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008. PMID: 18535258 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Shenfu injection and its main components on the contraction of isolated rat thoracic aortic rings.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 30;8(10):e78026. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078026. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24205074 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ANGULO J., RODRIGUEZ-MAÑAS L., PEIRO C., NEIRA M., MARIN J., SANCHEZ-FERRER C.F. Impairment of nitric oxide mediated relaxations in anaesthetized autoperfused streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 1998;358:529–537. - PubMed
-
- BURNETT A.L. Role of nitric oxide in the physiology of erection. Biol. Reprod. 1995;52:485–489. - PubMed
-
- BURNETT A.L., LOWENSTEIN C.J., BREDT D.S., CHANG T.S., SNYDER S.H. Nitric oxide: A physiologic mediator of penile erection. Science. 1992;257:401–403. - PubMed
-
- CERNADAS M.R., SANCHEZ DE MIGUEL L, GARCIA-DURAN M., GONZALEZ-FERNANDEZ F., MILLAS I., MONTON M., RODRIGO J., RICO L, FERNANDEZ P., DE FRUTOS T., RODRIGUEZ-FEO J.A., GUERRA J., CARAMELO C., CASADO S., LOPEZ-FARRE A. Expression of constitutive and inducible nitric oxide synthases in the vascular wall of young and aging rats. Circ. Res. 1998;83:279–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

