Nitric oxide enhances substance P-induced itch-associated responses in mice
- PMID: 12522091
- PMCID: PMC1573631
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705004
Nitric oxide enhances substance P-induced itch-associated responses in mice
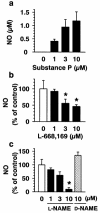
Abstract
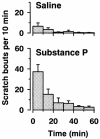
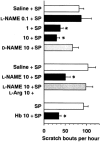
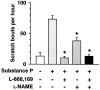
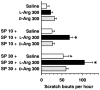
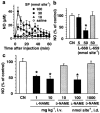
1 Substance P (SP) elicits itch and itch-associated responses in humans and mice, respectively. In mice, NK(1) tachykinin receptors are involved in SP-induced itch-associated responses, scratching, and mast cells do not play a critical role. The present study was conducted to elucidate the role of nitric oxide (NO) on SP-induced scratching in mice. 2 An intradermal injection of SP (100 nmol site(-1)) elicited scratching in mice, and it was suppressed by an intravenous injection of the NO synthase (NOS) inhibitor N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME), but not by its inactive enantiomer D-NAME. Intradermal injections of L-NAME (100 nmol site(-1)), another NOS inhibitor 7-nitroindazole (10 nmol site(-1)) and the NO scavenger haemoglobin (0.01-10 nmol site(-1)) also inhibited SP-induced scratching. 3 L-NAME (100 nmol site(-1)) did not affect scratching induced by an intradermal injection of 5-hydroxytryptamine (100 nmol site(-1)). 4 Intradermal injections of L-arginine (300 nmol site(-1)) and the NO donor (+/-)-(E)-4-ethyl-2-[(E)-hydroxyimino]-5-nitro-3-hexenamide (NOR3; 100 nmol site(-1)) increased scratching induced by SP. Intradermal injections of L-arginine (1-1000 nmol site(-1)) or NOR3 (1-100 nmol site(-1)) alone were without effects on scratching. 5 Intradermal injections of SP (10-100 nmol site(-1)) increased the intradermal concentration of NO in a dose-dependent manner in mice. An increase in NO levels induced by SP was inhibited by L-NAME and the NK(1) tachykinin receptor antagonist L-668,169, but not by the NK(2) tachykinin receptor antagonist L-659,877. 6 SP (1-10 micro M) elicited NO production in cultured human keratinocytes and the SP-induced NO production was inhibited by L-NAME and L-668,169. 7 We conclude that intradermal SP increases NO in the skin, possibly through the action on NK(1) tachykinin receptors on the epidermal keratinocytes and that NO enhances SP-induced itch-associated responses.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Substance P induction of itch-associated response mediated by cutaneous NK1 tachykinin receptors in mice.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998 Sep;286(3):1140-5. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998. PMID: 9732370
-
How important are NK1 receptors for influencing microvascular inflammation and itch in the skin? Studies using Phoneutria nigriventer venom.Vascul Pharmacol. 2006 Oct;45(4):209-14. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2005.08.025. Epub 2006 Jun 28. Vascul Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16914387
-
Involvement of nitric oxide in serotonin-induced scratching in mice.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015 Aug;40(6):647-52. doi: 10.1111/ced.12605. Epub 2015 Feb 22. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25703534
-
NK-1 Antagonists and Itch.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2015;226:237-55. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-44605-8_14. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25861784 Review.
-
[Mechanisms of cutaneous itch: new itch mediators and enhancement factors produced by keratinocytes].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2008 May;131(5):361-6. doi: 10.1254/fpj.131.361. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2008. PMID: 18480567 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Anti-pruritic effect of L-carnitine against chloroquine-induced pruritus mediated via nitric oxide pathway.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2024 May 22;25(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s40360-024-00748-4. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38778384 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral NMDA Receptor/NO System Blockage Inhibits Itch Responses Induced by Chloroquine in Mice.Acta Derm Venereol. 2017 May 8;97(5):571-577. doi: 10.2340/00015555-2617. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017. PMID: 28119997 Free PMC article.
-
Association between hair-induced oronasal inflammation and ulcerative dermatitis in C57BL/6 mice.Comp Med. 2011 Feb;61(1):13-9. Comp Med. 2011. PMID: 21819677 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the management of pruritus in chronic liver diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 May 21;23(19):3418-3426. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i19.3418. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28596678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Nitric Oxide in the Antipruritic Effect of WIN 55,212-2, a Cannabinoid Agonist.Basic Clin Neurosci. 2020 Jul-Aug;11(4):473-480. doi: 10.32598/bcn.9.10.465. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33613885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ANDOH T., KATSUBE N., MARUYAMA M., KURAISHI Y. Involvement of leukotriene B4 in substance P-induced itch-associated response in mice. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2001;117:1621–1626. - PubMed
-
- ANDOH T., KURAISHI Y. Quantitative determination of endogenous nitric oxide in the mouse skin in vivo by microdialysis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1997;332:279–282. - PubMed
-
- ANDOH T., KURAISHI Y. Intradermal leukotriene B4, but not prostaglandin E2, induces itch-associated responses in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998;353:93–96. - PubMed
-
- ANDOH T., KURAISHI Y. Involvement of blockade of leukotriene B4 action in anti-pruritic effects of emedastine in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000;406:149–152. - PubMed
-
- ANDOH T., KURAISHI Y. Inhibitory effects of azelastine on substance P-induced itch-associated response in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002;436:235–239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

