Comparison of signalling mechanisms involved in rat mesenteric microvessel contraction by noradrenaline and sphingosylphosphorylcholine
- PMID: 12522098
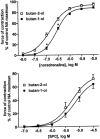
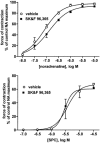
- PMCID: PMC1573654
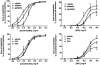
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705028
Comparison of signalling mechanisms involved in rat mesenteric microvessel contraction by noradrenaline and sphingosylphosphorylcholine
Abstract
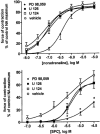
1 We have compared the signalling mechanisms involved in the pertussis toxin-sensitive and -insensitive contraction of rat isolated mesenteric microvessels elicited by sphingosylphosphorylcholine (SPC) and noradrenaline (NA), respectively. 2 The phospholipase D inhibitor butan-1-ol (0.3%), the store-operated Ca(2+) channel inhibitor SK>F 96,365 (10 microM), the tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein (10 microM), and the src inhibitor PP2 (10 microM) as well as the negative controls (0.3% butan-2-ol and 10 microM diadzein and PP3) had only little effect against either agonist. 3 Inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (wortmannin and LY 294,002, 10 microM each) or of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (PD 98,059 and U 126, 10 microM each) did not consistently attenuate NA- and SPC-induced contraction as compared to their vehicles or negative controls (LY 303,511 or U 124). 4 The phospholipase C inhibitor U 73,122 (10 microM) markedly inhibited the SPC- and NA-induced contraction (70% and 88% inhibition of the response to the highest NA and SPC concentration, respectively), whereas its negative control U 73,343 (10 microM) caused only less than 30% inhibition. 5 The rho-kinase inhibitors Y 27,632 (10 microM) and fasudil (30 microM) caused a rightward-shift of the NA concentration-response curve by 0.7-0.8 log units and reduced the response to 10 microM SPC by 88% and 83%, respectively. 6 These data suggest that SPC and NA, while acting on different receptors coupling to different G-protein classes, elicit contraction of rat mesenteric microvessels by similar signalling pathways including phospholipase C and rho-kinase.
Figures
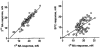



References
-
- ABURTO T., JINSI A., ZHU Q., DETH R.C. Involvement of protein kinase C activation in α2-adrenoceptor-mediated contractions of rabbit saphenous vein. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1995;277:35–44. - PubMed
-
- ALLEN B.G., WALSH M.P. The biochemical basis of the regulation of smooth-muscle contraction. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1994;19:362–368. - PubMed
-
- ANDERSON R.A., BORONENKOV I.V., DOUGHMAN S.D., KUNZ J., LOIJENS J.C. Phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinases, a multifaceted family of signaling enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:9907–9910. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

