Eosinophilic oesophagitis: a novel treatment using Montelukast
- PMID: 12524397
- PMCID: PMC1774975
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.52.2.181
Eosinophilic oesophagitis: a novel treatment using Montelukast
Abstract
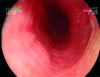
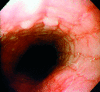
Background: Eosinophilic oesophagitis is a rarely diagnosed condition involving eosinophil infiltration of the oesophageal mucosa and creating significant symptoms of dysphagia. Failure to diagnose this disorder relates to reluctance to biopsy an apparently normal oesophagus. This is essential for histological diagnosis. To date, treatment success has been achieved only with corticosteroids. We describe here the use of an eosinophil stabilising agent Montelukast for the symptomatic relief of these patients.
Patients and methods: Twelve patients have been identified with this condition in our unit since 1995, after thorough investigation of their dysphagia. We commenced eight of these patients on the leukotriene receptor antagonist Montelukast to symptomatically improve their swallowing while avoiding the use of long term corticosteroids.
Results: Many of these patients had been previously misdiagnosed, and therefore inappropriately and unsuccessfully treated for an extensive period prior to referral to our unit. All patients were unresponsive to acid suppression therapy alone but showed improvement in their swallowing on Montelukast. Six of eight reported complete subjective improvement, five patients remaining completely asymptomatic on a maintenance regimen.
Conclusions: Eosinophilic oesophagitis is a disease that is often misdiagnosed due to lack of awareness and reluctance of clinicians to biopsy an apparently normal oesophagus in dysphagic patients, and therefore obtain a histological diagnosis. Investigation of these patients adds further evidence to this condition being a separate pathological state from gastro-oesophageal reflux and eosinophilic enteritis. Montelukast has been found to be of significant help in the symptomatic control of these patients while avoiding long term corticosteroids use.
Figures

Comment in
-
Eosinophilic oesophagitis: treatment using Montelukast.Gut. 2003 Aug;52(8):1228-9. doi: 10.1136/gut.52.8.1228. Gut. 2003. PMID: 12865292 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Treatment options for eosinophilic esophagitis: montelukast.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2004 Jun;6(3):190. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2004. PMID: 15128482 No abstract available.
References
-
- Attwood SEA, Smyrk TC, Demeester TR, et al. Esophageal eosinophilia with dysphagia. A distinct clinico-pathological syndrome. Dig Dis Sci 1993;38:109–16. - PubMed
-
- Lee RG. Marked eosinophilia in esophageal mucosal biopsies. Am J Surg Pathol 1986;10:75–86. - PubMed
-
- Dobbins JW, Sheahan DG, Behar J. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis with oesophageal involvement. Gastroenterology 1977;72:1312–16. - PubMed
-
- Goldman H, Proujansky R. Allergic proctitis and gastroenteritis in children: clinical and mucosal biopsy features in 53 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 1985;9:475–9. - PubMed
-
- Straumann HB, Spichtin R, Bernolli J, et al. Idiopathic eosinophilic oesophagitis. Swiss Med Wkly 1994;124:1419–29. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
