Anticitrullinated protein/peptide antibody assays in early rheumatoid arthritis for predicting five year radiographic damage
- PMID: 12525380
- PMCID: PMC1754441
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.62.2.120
Anticitrullinated protein/peptide antibody assays in early rheumatoid arthritis for predicting five year radiographic damage
Abstract
Objective: To study the value of antibodies to citrullinated proteins/peptides for predicting joint outcomes in patients with recent onset rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
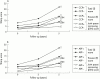
Methods: 191 patients with RA onset within the past year were followed up prospectively for five years. Serum samples obtained from 145 patients at baseline before disease modifying antirheumatic drug treatment were examined using three anticitrullinated protein/peptide antibody assays: antiperinuclear factor (APF) by indirect immunofluorescence (IIF), antikeratin antibodies (AKA) by IIF, and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) antibodies by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Radiographs of the hands and feet taken at baseline and after three and five years were evaluated using Sharp scores modified by van der Heijde.
Results: Anti-CCP ELISA was positive in 58.9% of patients. APF/anti-CCP agreement was 77%. The likelihood of a total Sharp score increase after five years was significantly greater among patients with anti-CCP antibodies (67%; odds ratio (OR) 2.5; 95% confidence interval (95% CI) 1.2 to 5.0) or APF (57%; OR 2.4; 95% CI 1.2 to 4.9) but not rheumatoid factor (RF; OR 0.7; 95% CI 0.3 to 1.5). Mean values for radiographic damage, erosion, and joint narrowing scores at the three times were significantly higher in patients with anti-CCP or APF than in those without. AKA did not significantly predict radiographic damage. In separate analyses of patients with and without RF, anti-CCP or APF was better than RF for predicting total joint damage and joint damage progression after five years.
Conclusion: Antibodies to citrullinated proteins/peptides determined early in the course of RA by APF IIF or anti-CCP ELISA are good predictors of radiographic joint damage. Further studies of clinical, laboratory, and genetic parameters are needed to improve RA outcome prediction in clinical practice.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous