Streptomycin and intracellular calcium modulate the response of single guinea-pig ventricular myocytes to axial stretch
- PMID: 12527736
- PMCID: PMC2342506
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.027573
Streptomycin and intracellular calcium modulate the response of single guinea-pig ventricular myocytes to axial stretch
Abstract
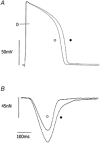
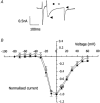
We tested the hypothesis that both stretch-activated channels (SACs) and intracellular calcium ([Ca(2+)](i)) are important in the electrical response of single guinea-pig ventricular myocytes to axial stretch. Myocytes were attached to carbon fibre transducers and stretched, sarcomere length increased by approximately 9 %, and there was a prolongation of the action potential duration. Streptomycin, a blocker of SACs, had no effect upon the shortening, [Ca(2+)](i) transients or action potentials of electrically stimulated, unstretched myocytes, at a concentration of 50 microM, but at 40 microM, prevented any stretch-induced increase in action potential duration. Under action potential clamp, stretch elicited a current with a linear current-voltage relationship that was inward at membrane potentials negative to its reversal potential of -30 mV, in 10 of 24 cells tested, and was consistent with the activation of non-specific, cationic SACs. This current was not seen in any stretched cells that were exposed to 40 microM streptomycin. However, exposure of cells to 5 microM BAPTA-AM, in order to reduce [Ca(2+)](i) transients, also abolished stretch-induced prolongation of the action potential. We conclude that both SACs and [Ca(2+)](i) are important in the electrical response of cardiac myocytes to stretch, and propose that stretch-induced changes in electrical activity and [Ca(2+)](i) may be linked by inter-dependent mechanisms.
Figures





References
-
- Alvarez B, Perez N, Ennis I, Camilion de Hurtagon M, Cingolani H. Mechanisms underlying the increase in Ca2+ transient that follow stretch of cardiac muscle: possible explanation of the Anrep effect. Circ Res. 1999;85:716–722. - PubMed
-
- Babuty D, Lab M. Heterogeneous changes of monophasic action potential induced by sustained stretch in atrium. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2001;12:323–329. - PubMed
-
- Belus A, White E. Effects of antibiotics on the contraction and Ca2+ transients of rat cardiac myocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001;412:121–126. - PubMed
-
- Bett GCL, Sachs F. Activation and inactivation of mechanosensistive currents in the chick heart. J Membr Biol. 2000a;173:237–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

