Vestibular actions on back and lower limb muscles during postural tasks in man
- PMID: 12527747
- PMCID: PMC2342524
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.030031
Vestibular actions on back and lower limb muscles during postural tasks in man
Abstract
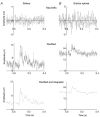
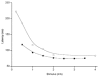
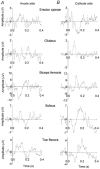
The vestibular system was activated by galvanic electrical stimulation in 19 normal subjects. With the head turned to one side so that the stimulating anode was on the posterior mastoid process, stimulation caused standing subjects to sway backwards in the sagittal plane. Electromyography showed bilateral activation of erector spinae, gluteus maximus, biceps femoris, soleus and intrinsic foot (toe flexor) muscles. When head direction or electrode polarity was reversed so that the anode was anterior, all those muscles became less active and the subjects swayed forwards. With the head facing forward, stimulation caused sideways sway in the coronal plane, towards the anode, with excitation of the erector spinae on the anode side and reduced activity on the cathode side. The limb muscles were activated on the side opposite the anode and showed complex responses on the anode side. Responses were detectable in the erectores spinae muscles in sitting subjects. No responses in limb muscles were detected in the sitting posture. Subject responses in erector spinae recorded at L3/L4 had latencies from 59 to 110 ms, using a 2 mA stimulus. Latencies in lower limb muscles were longer. The results suggest a role for the vestibular system and descending brain stem motor pathways to the erectores spinae muscles in the control of postural orientation of the back when sitting and standing. The conduction velocity in the motor pathway was estimated to be 13 +/- 10 m s(-1) (mean +/- S.D., n = 12 subjects).
Figures


References
-
- Andersson BJ, Jonsson B, Ortengren R. Myoelectric activity in individual lumbar erector spinae muscles in sitting. A study with surface and wire electrodes. Scand J Rehabil Med Suppl. 1974;3:91–108. - PubMed
-
- Andersson GB, Magnusson M. Neck vibration causes short-latency electromyographic activation of lower leg muscles in postural reactions of the standing human. Acta Otolaryngol. 2002;122:284–288. - PubMed
-
- Ardic FN, Latt LD, Redfern MS. Paraspinal muscle response to electrical vestibular stimulation. Acta Otolaryngol. 2000;120:39–46. - PubMed
-
- Britton T, Day B, Brown P, Rothwell J, Thompson P, Marsden C. Postural electromyographic responses in the arm and leg following galvanic vestibular stimulation in man. Exp Brain Res. 1993;94:143–151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

