Evaluation of the reliability and repeatability of automated milk urea nitrogen testing
- PMID: 12528831
- PMCID: PMC227029
Evaluation of the reliability and repeatability of automated milk urea nitrogen testing
Abstract
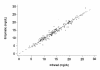
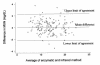
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the reliability (precision and accuracy), and repeatability of an infrared method of determining milk urea nitrogen. The reference method used for the reliability assessment was a wet-chemistry, enzymatic determination of milk urea nitrogen. Reliability and repeatability, as measured by concordance correlation coefficients, were 0.97 and 0.99, respectively.
Figures
References
-
- Godden SM, Lissemore KD, Kelton DF, Lumsden JH, Leslie KE, Walton JS. Analytic validation of an infrared milk urea assay and effects of sample acquisition factors on milk urea results. J Dairy Sci 2000;83:435–442. - PubMed
-
- Gustaffson AH. Current status concerning the use of milk urea concentration: analytical methods, use in different countries and how to utilize the results. Proceeding of the 30th Biennial Session of ICRA, Velhoven, The Netherlands, 1996:223–228.
-
- Grappin R, Packard VS, Ginn RE. Repeatability and accuracy of dye-binding and infrared methods for analyzing protein and other milk components. J Food Prot 1980;43:374–375. - PubMed
-
- Gustafsson AH, Carlsson J. Effects of silage quality, protein evaluation systems and milk urea content on milk yield and reproduction in dairy cows. Livest Prod Sci 1993;37:91–105.
-
- Lin Li-K. A concordance correlation coefficient to evaluate reproducibility. Biometrics 1989;45:255–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
