Genome rearrangements in mammalian evolution: lessons from human and mouse genomes
- PMID: 12529304
- PMCID: PMC430962
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.757503
Genome rearrangements in mammalian evolution: lessons from human and mouse genomes
Abstract
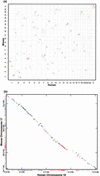
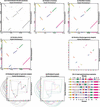
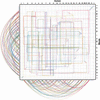
Although analysis of genome rearrangements was pioneered by Dobzhansky and Sturtevant 65 years ago, we still know very little about the rearrangement events that produced the existing varieties of genomic architectures. The genomic sequences of human and mouse provide evidence for a larger number of rearrangements than previously thought and shed some light on previously unknown features of mammalian evolution. In particular, they reveal that a large number of microrearrangements is required to explain the differences in draft human and mouse sequences. Here we describe a new algorithm for constructing synteny blocks, study arrangements of synteny blocks in human and mouse, derive a most parsimonious human-mouse rearrangement scenario, and provide evidence that intrachromosomal rearrangements are more frequent than interchromosomal rearrangements. Our analysis is based on the human-mouse breakpoint graph, which reveals related breakpoints and allows one to find a most parsimonious scenario. Because these graphs provide important insights into rearrangement scenarios, we introduce a new visualization tool that allows one to view breakpoint graphs superimposed with genomic dot-plots.
Figures

References
-
- Bafna V. and Pevzner, P.A., 1993. Genome rearrangements and sorting by reversals. In Proceedings of the 34th Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, pp. 148–157.
-
- ___, 1995. Sorting by reversals: Genome rearrangements in plant organelles and evolutionary history of X chromosome. Mol. Biol. Evol. 12: 239-246.
-
- ___, 1996. Genome rearrangements and sorting by reversals. SIAM J. Comput. 25: 272-289.
-
- Blanchette M., Kunisawa, T., and Sankoff, D. 1996. Parametric genome rearrangements. Gene 172: GC11-GC17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
