Deregulation of the Egfr/Ras signaling pathway induces age-related brain degeneration in the Drosophila mutant vap
- PMID: 12529440
- PMCID: PMC140241
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-05-0297
Deregulation of the Egfr/Ras signaling pathway induces age-related brain degeneration in the Drosophila mutant vap
Abstract
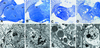
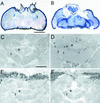
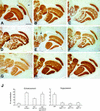
Ras signaling has been shown to play an important role in promoting cell survival in many different tissues. Here we show that upregulation of Ras activity in adult Drosophila neurons induces neuronal cell death, as evident from the phenotype of vacuolar peduncle (vap) mutants defective in the Drosophila RasGAP gene, which encodes a Ras GTPase-activating protein. These mutants show age-related brain degeneration that is dependent on activation of the EGF receptor signaling pathway in adult neurons, leading to autophagic cell death (cell death type 2). These results provide the first evidence for a requirement of Egf receptor activity in differentiated adult Drosophila neurons and show that a delicate balance of Ras activity is essential for the survival of adult neurons.
Figures
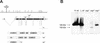

Similar articles
-
RasGAP mediates neuronal survival in Drosophila through direct regulation of Rab5-dependent endocytosis.J Cell Sci. 2014 Jul 1;127(Pt 13):2849-61. doi: 10.1242/jcs.139329. Epub 2014 May 9. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 24816559
-
Reduced growth of Drosophila neurofibromatosis 1 mutants reflects a non-cell-autonomous requirement for GTPase-Activating Protein activity in larval neurons.Genes Dev. 2006 Dec 1;20(23):3311-23. doi: 10.1101/gad.1466806. Epub 2006 Nov 17. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 17114577 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Caenorhabditis elegans vulval induction by gap-1 and by let-23 receptor tyrosine kinase.Genes Dev. 1997 Oct 15;11(20):2715-28. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.20.2715. Genes Dev. 1997. PMID: 9334333 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights from Drosophila into the Regulation of EGFR Signaling.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1652:37-42. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7219-7_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28791632 Review.
-
p120-Ras GTPase activating protein (RasGAP): a multi-interacting protein in downstream signaling.Biochimie. 2009 Mar;91(3):320-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2008.10.010. Epub 2008 Oct 30. Biochimie. 2009. PMID: 19022332 Review.
Cited by
-
Amyloid precursor proteins are protective in Drosophila models of progressive neurodegeneration.Neurobiol Dis. 2012 Apr;46(1):78-87. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2011.12.047. Epub 2012 Jan 10. Neurobiol Dis. 2012. PMID: 22266106 Free PMC article.
-
p120 Ras GTPase-activating protein associates with fibroblast growth factor receptors in Drosophila.Biochem J. 2004 Jun 15;380(Pt 3):767-74. doi: 10.1042/BJ20031848. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 15030317 Free PMC article.
-
Neurofibromin mediates FAK signaling in confining synapse growth at Drosophila neuromuscular junctions.J Neurosci. 2012 Nov 21;32(47):16971-81. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1756-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23175848 Free PMC article.
-
Using Drosophila Models and Tools to Understand the Mechanisms of Novel Human Cancer Driver Gene Function.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1167:15-35. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-23629-8_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31520347 Review.
-
Control of basal autophagy rate by vacuolar peduncle.PLoS One. 2019 Feb 8;14(2):e0209759. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209759. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30735514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashburner M. Drosophila: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1989.
-
- Barres BA, Schmid R, Sendtner M, Raff MC. Multiple extracellular signals are required for long-term oligodendrocyte survival. Development. 1993;118:283–295. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann A, Agapite J, McCall K, Steller H. The Drosophila gene hid is a direct molecular target of Ras-dependent survival signaling. Cell. 1998;95:331–341. - PubMed
-
- Bier E, Jan LY, Jan YN. rhomboid, a gene required for dorsoventral axis establishment and peripheral nervous system development in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1990;4:190–203. - PubMed
-
- Bonni A, Brunet A, West AE, Datta SR, Takasu MA, Greenberg ME. Cell survival promoted by the Ras-MAPK signaling pathway by transcription-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Science. 1999;286:1358–1362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

