Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and clinicopathologic features in human gastric adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 12532441
- PMCID: PMC4611321
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i2.250
Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and clinicopathologic features in human gastric adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Aim: To study the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) gene in gastric cancer and the relationship between COX-2 expression and clinicopathologic features of gastric cancer.
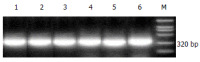
Methods: With reference to the expression of beta-actin gene, COX-2 mRNA level was examined in cancerous tissues and adjacent noncancerous mucosa from 33 patients by semiquantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Quantitation of relative band Adj volume counts was performed using molecular Analyst for windows software. The COX-2 index was determined from the band Adj volume counts ratio of COX-2 to constitutively expressed actin.
Results: The COX-2 index in gastric carcinoma was significantly higher than that in normal mucosa (0.5966+/-0.2659 vs 0.2979+/-0.171, u=5.4309, P<0.01). Significantly higher expression of COX-2 mRNA was also observed in patients with lymph node involvement than that in those without (0.6775+/-0.2486 vs 0.4105+/-0.2182, t=2.9341, P<0.01). Furthermore, the staging in the UICC TNM classification significantly correlated with COX-2 overexpression (F=3.656, P<0.05), the COX-2 index in stage III and IV was significantly higher than those in stage I and II (q=3.2728 and q=3.4906, P<0.05). The COX-2 index showed no correlation with patient's age, sex, blood group, tumor location, gross typing, depth of invasion, differentiation, and the greatest tumor dimension (P>0.05).
Conclusion: Expression of COX-2 mRNA in gastric carcinoma was significantly higher, which may enhance lymphatic metastasis in patients with gastric carcinoma. The staging in the UICC TNM classification was significantly correlated with COX-2 over-expression. COX-2 may contribute to progression of tumor in human gastric adenocarcinoma.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Depth of invasion parallels increased cyclooxygenase-2 levels in patients with gastric carcinoma.Cancer. 2001 May 15;91(10):1876-81. Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11346869
-
Expression of COX-2 in stomach cancers and its relation to their biological features.Dig Surg. 2003;20(2):107-14. doi: 10.1159/000069384. Dig Surg. 2003. PMID: 12686777
-
Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human gastric adenomas and adenocarcinomas.J Surg Oncol. 2001 Jan;76(1):26-30. doi: 10.1002/1096-9098(200101)76:1<26::aid-jso1005>3.0.co;2-a. J Surg Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11223821
-
Cyclooxygenase-2 and gastric carcinogenesis.APMIS. 2003 Oct;111(10):915-25. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0463.2003.1111001.x. APMIS. 2003. PMID: 14616542 Review.
-
Molecular and biologic basis of upper gastrointestinal malignancy. Gastric carcinoma.Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2002 Apr;11(2):273-91, viii. doi: 10.1016/s1055-3207(02)00004-2. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2002. PMID: 12424850 Review.
Cited by
-
Cloning of human 15ku selenoprotein gene from H9 T cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Aug;9(8):1777-80. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i8.1777. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12918119 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori regulates TLR4 and TLR9 during gastric carcinogenesis.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Sep 15;7(10):6950-5. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25400780 Free PMC article.
-
DNA polymerase zeta: new insight into eukaryotic mutagenesis and mammalian embryonic development.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Jun;9(6):1165-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1165. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12800216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of MTLC gene in gastric carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Oct;9(10):2160-3. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i10.2160. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 14562369 Free PMC article.
-
COX-2 Inhibitors and Gastric Cancer.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2014;2014:132320. doi: 10.1155/2014/132320. Epub 2014 Oct 12. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2014. PMID: 25371669 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sawaoka H, Kawano S, Tsuji S, Tsujii M, Murata H, Hori M. Effects of NSAIDs on proliferation of gastric cancer cells in vitro: possible implication of cyclooxygenase-2 in cancer development. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1998;27 Suppl 1:S47–S52. - PubMed
-
- Uefuji K, Ichikura T, Shinomiya N, Mochizuki H. Induction of apoptosis by JTE-522, a specific cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, in human gastric cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res. 2000;20:4279–4284. - PubMed
-
- Sawaoka H, Kawano S, Tsuji S, Tsujii M, Gunawan ES, Takei Y, Nagano K, Hori M. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors suppress the growth of gastric cancer xenografts via induction of apoptosis in nude mice. Am J Physiol. 1998;274:G1061–G1067. - PubMed
-
- Wu QM, Li SB, Wang Q, Wang SH, Li XB, Liu CZ. The expression of COX-2 in esophageal carcinoma and its relation to clinicopathologic characteristics. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2001;9:11–14.
-
- Chan G, Boyle JO, Yang EK, Zhang F, Sacks PG, Shah JP, Edelstein D, Soslow RA, Koki AT, Woerner BM, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is up-regulated in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer Res. 1999;59:991–994. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

