The effect of famotidine on gastroesophageal and duodeno-gastro-esophageal refluxes in critically ill patients
- PMID: 12532466
- PMCID: PMC4611346
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i2.356
The effect of famotidine on gastroesophageal and duodeno-gastro-esophageal refluxes in critically ill patients
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of famotidine on gastroesophageal reflux (GER) and duodeno-gastro-esophageal reflux (DGER) and to explore it's possible mechanisms. To identify the relevant factors of the reflux.
Methods: Nineteen critically ill patients were consecutively enrolled in the study. Dynamic 24 hours monitoring of GER and DGER before and after administration of famotidine was performed. The parameters of gastric residual volume, multiple organ disorder syndrome (MODS) score, acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II (APACHE II) score and PEEP were recorded. Paired t test; Wilcoxon signed ranks test and Univariate analysis with Spearman's rank correlation were applied to analyse the data.
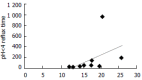
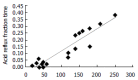
Results: Statistical significance of longest acid reflux, reflux time of pH<4 and fraction time of acid reflux was observed in ten critically ill patients before and after administration. P value is 0.037, 0.005, 0.005 respectively. Significance change of all bile reflux parameters was observed before and after administration. P value is 0.007,0.024, 0.005, 0.007, 0.005. GER has positive correlation with APACHE II score and gastric residual volume with correlation coefficient of 0.720, 0.932 respectively.
Conclusion: GER and DGER are much improved after the administration of famotidine. GER is correlated with APACHE II score and gastric residual volume.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tolerance to H2 receptor antagonist correlates well with the decline in efficacy against gastroesophageal reflux in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006 Oct;21(10):1581-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04323.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006. PMID: 16928220
-
Comparison of omeprazole and famotidine on esophageal pH in patients with moderate to severe esophagitis: a cross-over study.Am J Gastroenterol. 1994 May;89(5):717-21. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994. PMID: 8172144
-
Gastroesophageal reflux disease poorly responsive to single-dose proton pump inhibitors in patients without Barrett's esophagus: acid reflux, bile reflux, or both?Am J Gastroenterol. 2004 Jun;99(6):981-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.04171.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15180713
-
Importance of duodeno-gastro-esophageal reflux in the medical outpatient practice.Hepatogastroenterology. 1999 Jan-Feb;46(25):40-7. Hepatogastroenterology. 1999. PMID: 10228763 Review.
-
Famotidine in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).Hepatogastroenterology. 1992 Feb;39 Suppl 1:24-6. Hepatogastroenterology. 1992. PMID: 1577391 Review.
Cited by
-
Gastric residual volume and aspiration in critically ill patients receiving gastric feedings.Am J Crit Care. 2008 Nov;17(6):512-9; quiz 520. Am J Crit Care. 2008. PMID: 18978236 Free PMC article.
-
Gastroesophageal reflux in mechanically ventilated pediatric patients and its relation to ventilator-associated pneumonia.Crit Care. 2009;13(5):R164. doi: 10.1186/cc8134. Epub 2009 Oct 19. Crit Care. 2009. PMID: 19840378 Free PMC article.
-
Gastroesophageal reflux in critically ill children: a review.ISRN Gastroenterol. 2013;2013:824320. doi: 10.1155/2013/824320. Epub 2013 Jan 31. ISRN Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23431462 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Niederau C, Lübke H, Schumacher B, Strohmeyer G. [Endoscopy in the intensive care unit] Z Gastroenterol. 1994;32:465–469. - PubMed
-
- Tomonaga T, Awad ZT, Filipi CJ, Hinder RA, Selima M, Tercero F, Marsh RE, Shiino Y, Welch R. Symptom predictability of reflux-induced respiratory disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2002;47:9–14. - PubMed
-
- Saxe JM, Ledgerwood AM, Lucas CE, Lucas WF. Lower esophageal sphincter dysfunction precludes safe gastric feeding after head injury. J Trauma. 1994;37:581–584; discussion 581-584;. - PubMed
-
- Richter JE, Bradley LA, DeMeester TR, Wu WC. Normal 24-hr ambulatory esophageal pHvalues. Influence of study center, pHelectrode, age, and gender. Dig Dis Sci. 1992;37:849–856. - PubMed
-
- Vaezi MF, Richter JE. Role of acid and duodenogastroesophageal reflux in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 1996;111:1192–1199. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

