c-MYC apoptotic function is mediated by NRF-1 target genes
- PMID: 12533512
- PMCID: PMC195978
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1032503
c-MYC apoptotic function is mediated by NRF-1 target genes
Abstract
A detailed understanding of the signaling pathways by which c-Myc elicits apoptosis has proven elusive. In the current study, we have evaluated whether the activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic signaling pathway is linked to c-Myc induction of a subset of genes involved in mitochondrial biogenesis. Cytochrome c and other nuclear-encoded mitochondrial genes are regulated by the transcription factor nuclear respiratory factor-1 (NRF-1). The consensus binding sequence (T/C)GCGCA(C/T)GCGC(A/G) of NRF-1 includes a noncanonical CA(C/T)GCG Myc:MAX binding site. In this study, we establish a link between the induction of NRF-1 target genes and sensitization to apoptosis on serum depletion. We demonstrate, by using Northern analysis, transactivation assays, and in vitro and in vivo promoter binding assays that cytochrome c is a direct target of c-Myc. Like c-Myc, NRF-1 overexpression sensitizes cells to apoptosis on serum depletion. We also demonstrate that selective interference with c-Myc induction of NRF-1 target genes by using a dominant-negative NRF-1 prevented c-Myc-induced apoptosis, without affecting c-Myc-dependent proliferation. These results suggest that c-myc expression leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis by deregulating genes involved in mitochondrial function.
Figures
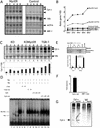


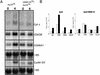

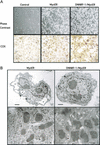

Comment in
-
Myc's mastery of mitochondrial mischief.Cell Cycle. 2003 Jan-Feb;2(1):11-3. doi: 10.4161/cc.2.1.275. Cell Cycle. 2003. PMID: 12695675 Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Sequential serum-dependent activation of CREB and NRF-1 leads to enhanced mitochondrial respiration through the induction of cytochrome c.J Biol Chem. 2000 Apr 28;275(17):13134-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.17.13134. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10777619
-
Control of mitochondrial transcription specificity factors (TFB1M and TFB2M) by nuclear respiratory factors (NRF-1 and NRF-2) and PGC-1 family coactivators.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Feb;25(4):1354-66. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.4.1354-1366.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15684387 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the human mitochondrial transcription factor A gene by nuclear respiratory factors: a potential regulatory link between nuclear and mitochondrial gene expression in organelle biogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1309-13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1309. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994. PMID: 8108407 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial transcription factor A (mtTFA) and diabetes.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2001 Dec;54 Suppl 2:S3-9. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8227(01)00330-8. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2001. PMID: 11733104 Review.
-
Nuclear activators and coactivators in mammalian mitochondrial biogenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Jun 7;1576(1-2):1-14. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4781(02)00343-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12031478 Review.
Cited by
-
Intragenic Transcriptional cis-Antagonism Across SLC6A3.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Jun;56(6):4051-4060. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1357-5. Epub 2018 Sep 27. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30259411 Free PMC article.
-
The Krebs cycle meets the cell cycle: mitochondria and the G1-S transition.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jul 21;106(29):11825-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906430106. Epub 2009 Jul 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19617546 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Mitochondrial Quality Control as a Therapeutic Target.Pharmacol Rev. 2016 Jan;68(1):20-48. doi: 10.1124/pr.115.011502. Pharmacol Rev. 2016. PMID: 26589414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogenic control of mitochondrial function and biogenesis.J Cell Biochem. 2008 Dec 15;105(6):1342-51. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21936. J Cell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 18846505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
15q11.2-13 duplication, mitochondrial dysfunction, and developmental disorders.J Child Neurol. 2009 Oct;24(10):1316-20. doi: 10.1177/0883073809333531. Epub 2009 Jun 17. J Child Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19535813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becjker T, Burgess S, Amsterdam A, Allende M, Hopkins N. not really finished is crucial for development of the zebrafish outer retina and encodes a transcription factor highly homologous to human nuclear respiratory factor-1 and avian initiation binding repressor. Development. 1998;125:4369–4378. - PubMed
-
- Bejarano M, Cornvik A, Brijker S, Asker C, Osorio L, Henriksson M. Inhibition of cell growth and apoptosis by inducible expression of the transcriptional repressor Mad1. Exp Cell Res. 2000;260:61–72. - PubMed
-
- Bissonnette R, Echeverri F, Mahboubi A, Green D. Apoptotic cell death induced by c-myc is inhibited by bcl-2. Nature. 1992;359:552–556. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
