A photochemical approach to the lipid accessibility of engineered cysteinyl residues
- PMID: 12533666
- PMCID: PMC298696
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0237311100
A photochemical approach to the lipid accessibility of engineered cysteinyl residues
Abstract
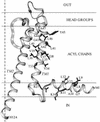
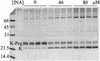
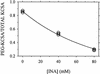
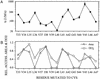
Ordinary electrophilic reagents react too slowly in a nonpolar environment to be useful for the determination of the accessibility to lipid of continuous stretches of residues mutated to cysteine. By contrast, photoactivated 5-iodonaphthyl-1-azide (INA) reacted readily with 2-mercaptoethanol and dodecanethiol in nonpolar solvents and in liposomes. Continuous stretches of residues in the amphipathic N-terminal helix and first transmembrane helix of the bacterial potassium channel KcsA were replaced with cysteine, and the mutants were expressed in Escherichia coli and isolated in inner membranes. These membranes were dissolved in detergent and reconstituted into asolectin liposomes incorporating INA. The extent of light-induced reaction of INA with each cysteine was assayed by subsequent reaction with the gel-shifting, SH-specific methoxy-polyethylene glycol-2-pyridine disulfide. The pattern of apparent second-order rate constants for the photoreactions of eight substituted cysteines in the N-terminal helix conformed to other measures of lipid exposure. The pattern of the rate constants for the photoreactions of 15 cysteines in the first transmembrane helix had peaks every third residue, which partly conformed to other measures of lipid exposure.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Reactions of cysteines substituted in the amphipathic N-terminal tail of a bacterial potassium channel with hydrophilic and hydrophobic maleimides.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Sep 3;99(18):11605-10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.192439299. Epub 2002 Aug 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12189213 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of C-terminal protein domains and protein-lipid interactions on tetramerization and stability of the potassium channel KcsA.Biochemistry. 2004 Nov 30;43(47):14924-31. doi: 10.1021/bi048889+. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15554699
-
Sulfhydryl chemistry detects three conformations of the lipid binding region of Escherichia coli pyruvate oxidase.Biochemistry. 1997 Sep 30;36(39):11564-73. doi: 10.1021/bi9709102. Biochemistry. 1997. PMID: 9305946
-
Interactions of phospholipids with the potassium channel KcsA.Biophys J. 2002 Oct;83(4):2026-38. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(02)73964-7. Biophys J. 2002. PMID: 12324421 Free PMC article.
-
Detergent-labile, supramolecular assemblies of KcsA: relative abundance and interactions involved.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Feb;1828(2):193-200. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.09.020. Epub 2012 Sep 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23022492
Cited by
-
Inactivation of Zika Virus by Photoactive Iodonaphthyl Azide Preserves Immunogenic Potential of the Virus.Pathogens. 2019 Oct 12;8(4):188. doi: 10.3390/pathogens8040188. Pathogens. 2019. PMID: 31614887 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

