Expression of ICOS in vivo defines CD4+ effector T cells with high inflammatory potential and a strong bias for secretion of interleukin 10
- PMID: 12538658
- PMCID: PMC2193816
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20020632
Expression of ICOS in vivo defines CD4+ effector T cells with high inflammatory potential and a strong bias for secretion of interleukin 10
Abstract
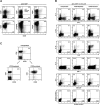
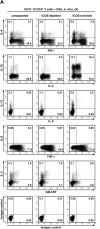
The studies performed to date analyzed the overall participation of the inducible costimulator (ICOS) in model diseases, but did not yield information on the nature and function of ICOS-expressing T cells in vivo. We examined ICOS(+) T cells in the secondary lymphoid organs of nonmanipulated mice, in the context of an "unbiased" immune system shaped by environmental antigens. Using single cell analysis, ICOS(low) cells were found to be loosely associated with the early cytokines interleukin (IL)-2, IL-3, IL-6, and interferon (IFN)-gamma. ICOS(medium) cells, the large majority of ICOS(+) T cells in vivo, were very tightly associated with the synthesis of the T helper type 2 (Th2) cytokines IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, and these cells exhibited potent inflammatory effects in vivo. In contrast, ICOS(high) T cells were highly and selectively linked to the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. Overall, these data seem to indicate that ICOS cell surface density serves as a regulatory mechanism for the release of cytokines with different immunological properties. Further in vivo functional experiments with in vitro-activated T cells strongly suggested that the ICOS(+) population, although representing in vivo only around 10% of T cells bearing early or late activation markers, nevertheless encompasses virtually all effector T cells, a finding with major diagnostic and therapeutic implications.
Figures








References
-
- Hutloff, A., A.M. Dittrich, K.C. Beier, B. Eljaschewitsch, R. Kraft, I. Anagnostopoulos, and R.A. Kroczek. 1999. ICOS is an inducible T-cell co-stimulator structurally and functionally related to CD28. Nature. 397:263–266. - PubMed
-
- Yoshinaga, S.K., J.S. Whoriskey, S.D. Khare, U. Sarmiento, J. Guo, T. Horan, G. Shih, M. Zhang, M.A. Coccia, T. Kohno, et al. 1999. T-cell co-stimulation through B7RP-1 and ICOS. Nature. 402:827–832. - PubMed
-
- Coyle, A.J., S. Lehar, C. Lloyd, J. Tian, T. Delaney, S. Manning, T. Nguyen, T. Burwell, H. Schneider, J.A. Gonzalo, et al. 2000. The CD28-related molecule ICOS is required for effective T cell-dependent immune responses. Immunity. 13:95–105. - PubMed
-
- McAdam, A.J., T.T. Chang, A.E. Lumelsky, E.A. Greenfield, V.A. Boussiotis, J.S. Duke-Cohan, T. Chernova, N. Malenkovich, C. Jabs, V.K. Kuchroo, et al. 2000. Mouse inducible costimulatory molecule (ICOS) expression is enhanced by CD28 costimulation and regulates differentiation of CD4+ T cells. J. Immunol. 165:5035–5040. - PubMed
-
- Özkaynak, E., W. Gao, N. Shemmeri, C. Wang, J.C. Gutierrez-Ramos, J. Amaral, S. Qin, J.B. Rottman, A.J. Coyle, and W.W. Hancock. 2001. Importance of ICOS-B7RP-1 costimulation in acute and chronic allograft rejection. Nat. Immunol. 2:591–596. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

